Keane 2011 Parkinsons Dis
| Keane PC, Kurzawa M, Blain PG, Morris CM (2011) Mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsons Dis 2011:716871. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/716871 |
Keane PC, Kurzawa M, Blain PG, Morris CM (2011) Parkinsons Dis
Abstract: Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive, neurodegenerative condition that has increasingly been linked with mitochondrial dysfunction and inhibition of the electron transport chain. This inhibition leads to the generation of reactive oxygen species and depletion of cellular energy levels, which can consequently cause cellular damage and death mediated by oxidative stress and excitotoxicity. A number of genes that have been shown to have links with inherited forms of PD encode mitochondrial proteins or proteins implicated in mitochondrial dysfunction, supporting the central involvement of mitochondria in PD. This involvement is corroborated by reports that environmental toxins that inhibit the mitochondrial respiratory chain have been shown to be associated with PD. This paper aims to illustrate the considerable body of evidence linking mitochondrial dysfunction with neuronal cell death in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) of PD patients and to highlight the important need for further research in this area.
• Bioblast editor: Gnaiger E
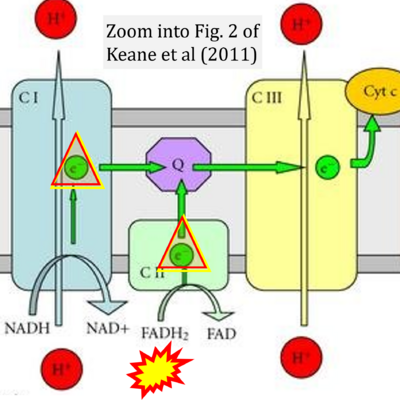
Correction: FADH2 and Complex II
- FADH2 is shown as the substrate feeding electrons into Complex II (CII). This is wrong and requires correction - for details see Gnaiger (2024).
- Gnaiger E (2024) Complex II ambiguities ― FADH2 in the electron transfer system. J Biol Chem 300:105470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105470 - »Bioblast link«
Labels:
Enzyme: Complex II;succinate dehydrogenase