Kezic 2016 Oxid Med Cell Longev
| Kezic A, Spasojevic I, Lezaic V, Bajcetic M (2016) Mitochondria-targeted antioxidants: future perspectives in kidney ischemia reperfusion injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:2950503. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2950503 |
Kezic A, Spasojevic I, Lezaic V, Bajcetic M (2016) Oxid Med Cell Longev
Abstract: Kidney ischemia/reperfusion injury emerges in various clinical settings as a great problem complicating the course and outcome. Ischemia/reperfusion injury is still an unsolved puzzle with a great diversity of investigational approaches, putting the focus on oxidative stress and mitochondria. Mitochondria are both sources and targets of ROS. They participate in initiation and progression of kidney ischemia/reperfusion injury linking oxidative stress, inflammation, and cell death. The dependence of kidney proximal tubule cells on oxidative mitochondrial metabolism makes them particularly prone to harmful effects of mitochondrial damage. The administration of antioxidants has been used as a way to prevent and treat kidney ischemia/reperfusion injury for a long time. Recently a new method based on mitochondria-targeted antioxidants has become the focus of interest. Here we review the current status of results achieved in numerous studies investigating these novel compounds in ischemia/reperfusion injury which specifically target mitochondria such as MitoQ, Szeto-Schiller (SS) peptides (Bendavia), SkQ1 and SkQR1, and superoxide dismutase mimics. Based on the favorable results obtained in the studies that have examined myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury, ongoing clinical trials investigate the efficacy of some novel therapeutics in preventing myocardial infarct. This also implies future strategies in preventing kidney ischemia/reperfusion injury.
• Bioblast editor: Gnaiger E
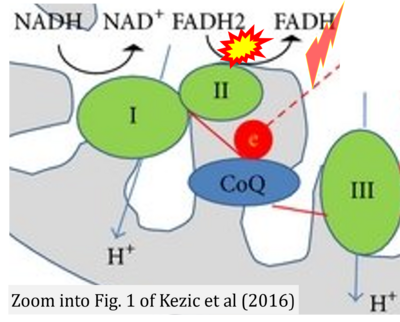
Correction: FADH2 and Complex II
- FADH2 is shown as the substrate feeding electrons into Complex II (CII). This is wrong and requires correction - for details see Gnaiger (2024).
- Gnaiger E (2024) Complex II ambiguities ― FADH2 in the electron transfer system. J Biol Chem 300:105470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105470 - »Bioblast link«
Labels:
Enzyme: Complex II;succinate dehydrogenase