Difference between revisions of "Fatty acid oxidation pathway control state"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{MitoPedia | {{MitoPedia | ||
|abbr=FAO, F | |abbr=FAO, F | ||
|description=[[File:SUIT- | |description=[[File:SUIT-catg F.jpg|right|300px|F-junction]] | ||
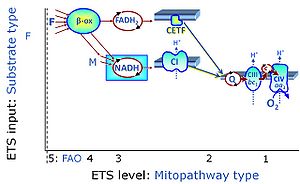
In the fatty acid oxidation or '''FAO'''-linked substrate state, one or several fatty acids are supplied to feed electrons into the [[F-junction]] through [[fatty acyl CoA dehydrogenase]] (reduced form [[FADH2]]), to [[electron transferring flavoprotein]] (CETF), and further through the [[Q-junction]] to [[Complex III]] (CIII). FAO not only depends on electron transfer through the F-junction (which is typically rate-limiting) but simultaneously generates NADH and thus depends on [[N-junction]] throughput. Hence FAO can be inhibited completely by inhibition of [[Complex I]] (CI). In addition and independent of this source of NADH, the type N substrate malate is required as a co-substrate for FAO in mt-preparations, since accumulation of AcetylCo inhibits FAO in the absence of malate. Malate is oxidized in a reaction catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase to oxaloacetate (yielding NADH), which then stimulates the entry of AcetylCo into the TCA cycle catalyzed by citrate synthase. | In the fatty acid oxidation or '''FAO'''-linked substrate state, one or several fatty acids are supplied to feed electrons into the [[F-junction]] through [[fatty acyl CoA dehydrogenase]] (reduced form [[FADH2]]), to [[electron transferring flavoprotein]] (CETF), and further through the [[Q-junction]] to [[Complex III]] (CIII). FAO not only depends on electron transfer through the F-junction (which is typically rate-limiting) but simultaneously generates NADH and thus depends on [[N-junction]] throughput. Hence FAO can be inhibited completely by inhibition of [[Complex I]] (CI). In addition and independent of this source of NADH, the type N substrate malate is required as a co-substrate for FAO in mt-preparations, since accumulation of AcetylCo inhibits FAO in the absence of malate. Malate is oxidized in a reaction catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase to oxaloacetate (yielding NADH), which then stimulates the entry of AcetylCo into the TCA cycle catalyzed by citrate synthase. | ||
|info=[[Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways]] | |info=[[Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways]] | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|mitopedia concept=Respiratory state, SUIT state | |mitopedia concept=Respiratory state, SUIT state | ||
}} | }} | ||
::::» [[Talk:Fatty acid oxidation |O2k-Network discussion forum: fatty acids used in permeabilized fibre assays]] | ::::» [[Talk:Fatty acid oxidation |O2k-Network discussion forum: fatty acids used in permeabilized fibre assays]] | ||
::::» [[F-junction]] | ::::» [[F-junction]] | ||
Revision as of 23:34, 21 August 2016
- high-resolution terminology - matching measurements at high-resolution
Fatty acid oxidation pathway control state
Description
In the fatty acid oxidation or FAO-linked substrate state, one or several fatty acids are supplied to feed electrons into the F-junction through fatty acyl CoA dehydrogenase (reduced form FADH2), to electron transferring flavoprotein (CETF), and further through the Q-junction to Complex III (CIII). FAO not only depends on electron transfer through the F-junction (which is typically rate-limiting) but simultaneously generates NADH and thus depends on N-junction throughput. Hence FAO can be inhibited completely by inhibition of Complex I (CI). In addition and independent of this source of NADH, the type N substrate malate is required as a co-substrate for FAO in mt-preparations, since accumulation of AcetylCo inhibits FAO in the absence of malate. Malate is oxidized in a reaction catalyzed by malate dehydrogenase to oxaloacetate (yielding NADH), which then stimulates the entry of AcetylCo into the TCA cycle catalyzed by citrate synthase.
Abbreviation: FAO, F
Reference: Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways
MitoPedia concepts:
Respiratory state,
SUIT state
FAO(L)
- FAOL: FAO in the LEAK state
FAO(P)
- FAOP: FAO in the OXPHOS state
FAO(E)
- FAOE: FAO in the ETS state
O2k-Publications: FAO
Sort in ascending/descending order by a click on one of the small symbols in squares below. Default sorting: chronological. Empty fields appear first in ascending order.
O2k-Publications: FAO - Abstracts
Sort in ascending/descending order by a click on one of the small symbols in squares below.