Difference between revisions of "R-L net ROUTINE capacity"
Beno Marija (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{MitoPedia concepts | {{MitoPedia concepts | ||
|mitopedia concept=Respiratory state, Recommended | |mitopedia concept=Respiratory state, Recommended | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{MitoPedia methods}} | {{MitoPedia methods}} | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
== Compare == | == Compare == | ||
* [[Free OXPHOS capacity]] (mt-preparations) | * [[Free OXPHOS capacity]] (mt-preparations) | ||
* [[Free ET | * [[Free ET capacity]] | ||
Revision as of 10:59, 3 June 2020
Description
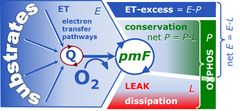
![]() The free ROUTINE activity, ≈R, is ROUTINE respiration corrected for LEAK respiration, ≈R = R-L. ≈R is the respiratory activity available for phosphorylation of ADP to ATP. Oxygen consumption in the ROUTINE state of respiration measured in intact cells, therefore, is partitioned into the free ROUTINE activity, ≈R, strictly coupled to phosphorylation, ~P, and nonphosphorylating LEAK respiration, LR, compensating for proton leaks, slip and cation cycling: R = ≈R+LR. It is frequently assumed that LEAK respiration, L, as measured in the LEAK state, overestimates the LEAK component of respiration, LR, as measured in the ROUTINE state, particularly if the protonmotive force is not adjusted to equivalent levels in L and LR. However, if the LEAK component increases with enzyme turnover during R, the low enzyme turnover during L may counteract the effect of the higher Δpmt.
The free ROUTINE activity, ≈R, is ROUTINE respiration corrected for LEAK respiration, ≈R = R-L. ≈R is the respiratory activity available for phosphorylation of ADP to ATP. Oxygen consumption in the ROUTINE state of respiration measured in intact cells, therefore, is partitioned into the free ROUTINE activity, ≈R, strictly coupled to phosphorylation, ~P, and nonphosphorylating LEAK respiration, LR, compensating for proton leaks, slip and cation cycling: R = ≈R+LR. It is frequently assumed that LEAK respiration, L, as measured in the LEAK state, overestimates the LEAK component of respiration, LR, as measured in the ROUTINE state, particularly if the protonmotive force is not adjusted to equivalent levels in L and LR. However, if the LEAK component increases with enzyme turnover during R, the low enzyme turnover during L may counteract the effect of the higher Δpmt.
Abbreviation: ≈R
Reference: Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways
MitoPedia concepts:
Respiratory state,
Recommended
MitoPedia topics:
EAGLE
Communicated by Gnaiger E 2014-09-21, edited 2015-01-19.
Compare
- Free OXPHOS capacity (mt-preparations)
- Free ET capacity
