Difference between revisions of "Gnaiger 1977 Invertebrate anoxibiosis"
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
|additional=Microcalorimetry, Malic enzyme | |additional=Microcalorimetry, Malic enzyme | ||
}} | }} | ||
* [[Malic enzyme]] | |||
Revision as of 06:28, 8 August 2014
| Gnaiger E (1977) Thermodynamic considerations of invertebrate anoxibiosis. In: Applications of calorimetry in life sciences. Lamprecht I, Schaarschmidt B (eds), de Gruyter, Berlin: 281-303. |
Gnaiger E (1977) de Gruyter
Abstract:
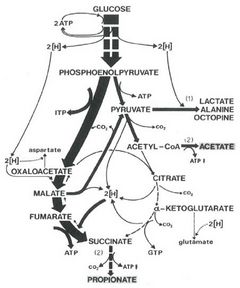
New insight into the biochemical mechanism of invertebrate anoxibiosis made possible the calculation of the free-energy changes associated with the generation of high-energy bonds in nucleoside triphosphates (ATP, GTP, ITP) under anoxic conditions. The values obtained are compared with thermodynamic data of aerobic and fermentative energy production, and indicate a selection towards increased energetic efficiency of biochemical pathways leading to less toxic and readily excretable end products in anoxibiotic invertebrates. The thermodynamic model is mainly based upon a metabolic scheme elaborated on intertidal bivalves by de Zwaan et al, benthic oligochaetes and fresh-water bivalves. It may provide a general hypothesis for the energetic processes which operate in a variety of ecological and taxonomic groups of anoxibiotic animals.
• O2k-Network Lab: AT_Innsbruck_Gnaiger E
Labels: MiParea: Respiration, Comparative MiP;environmental MiP
Stress:Hypoxia
Preparation: Intact Organism"Intact Organism" is not in the list (Intact organism, Intact organ, Permeabilized cells, Permeabilized tissue, Homogenate, Isolated mitochondria, SMP, Chloroplasts, Enzyme, Oxidase;biochemical oxidation, ...) of allowed values for the "Preparation" property.
Regulation: Aerobic glycolysis, ATP, Coupling efficiency;uncoupling
Microcalorimetry, Malic enzyme