Description
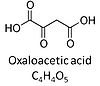
Oxaloacetic acid, C4H4O5, occurs under physiological conditions as the anion oxaloacetate2-, Oa. Oxaloacetate is formed from malate by MDH, cannot permeate the inner mt-membrane and has no carrier. Oxaloacetate reacts with acetyl-CoA through citrate synthase to form citrate, or with glutamate through transaminase to form oxoglutarate and aspartate.
Abbreviation: Oa
Reference: Gnaiger 2012 MitoPathways
MitoPedia topics: Substrate and metabolite
Labels:
Enzyme: TCA Cycle and Matrix Dehydrogenases"TCA Cycle and Matrix Dehydrogenases" is not in the list (Adenine nucleotide translocase, Complex I, Complex II;succinate dehydrogenase, Complex III, Complex IV;cytochrome c oxidase, Complex V;ATP synthase, Inner mt-membrane transporter, Marker enzyme, Supercomplex, TCA cycle and matrix dehydrogenases, ...) of allowed values for the "Enzyme" property. Regulation: Substrate; Glucose; TCA Cycle"Substrate; Glucose; TCA Cycle" is not in the list (Aerobic glycolysis, ADP, ATP, ATP production, AMP, Calcium, Coupling efficiency;uncoupling, Cyt c, Flux control, Inhibitor, ...) of allowed values for the "Respiration and regulation" property.