Difference between revisions of "Q-junction"
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
{{MitoPedia topics|type=Respiration | {{MitoPedia topics|type=Respiration | ||
}} | }} | ||
[[File:Hatefi 1962 CI | [[File:Hatefi 1962 CI&II 2012.jpg|right|500px|Q-junction]] | ||
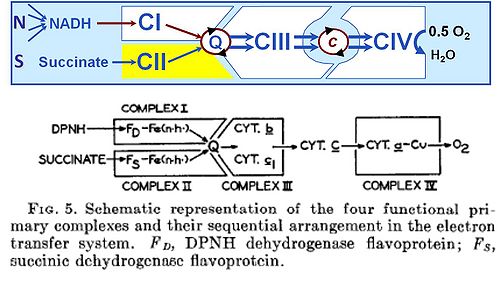
Convergent CI&II-linked electron flow at the Q-junction, exerting an additive effect on flux, versus electron gaiting for separation of single input pathways (upper panel: [[Gnaiger 2009 Int J Biochem Cell Biol |Gnaiger 2009]]; lower panel: [[Hatefi 1962 J Biol Chem-XLII]]). From Fig. 1.5 in [[Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways]]. | Convergent CI&II-linked electron flow at the Q-junction, exerting an additive effect on flux, versus electron gaiting for separation of single input pathways (upper panel: [[Gnaiger 2009 Int J Biochem Cell Biol |Gnaiger 2009]]; lower panel: [[Hatefi 1962 J Biol Chem-XLII]]). From Fig. 1.5 in [[Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways]]. | ||
* [[O2k-Publications: Q-Junction Effect]] | * [[O2k-Publications: Q-Junction Effect]] | ||
Revision as of 15:58, 14 August 2014
Description
The Q-junction is a junction for convergent electron flow in the electron transfer system (ETS) from Complex I (CI), Complex II (CII), electron-transferring flavoprotein (CETF), glycerophosphate dehydrogenase complex (CGpDH), choline dehydrogenase and other enzyme complexes into the Q-cycle (ubiquinol/ubiquinone), and further to Complex III (CIII).
Abbreviation: Q
Reference: Gnaiger 2009 Int J Biochem Cell Biol, Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways
MitoPedia methods:
Respirometry
Convergent CI&II-linked electron flow at the Q-junction, exerting an additive effect on flux, versus electron gaiting for separation of single input pathways (upper panel: Gnaiger 2009; lower panel: Hatefi 1962 J Biol Chem-XLII). From Fig. 1.5 in Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways.