Difference between revisions of "ROUTINE respiration"
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
|type=Respiration | |type=Respiration | ||
}} | }} | ||
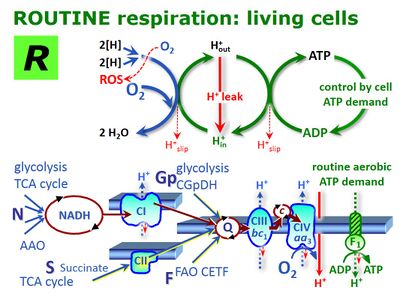
[[File:ROUTINE.jpg| | [[File:ROUTINE.jpg|400px|thumb|Coupled energy cycles and and proton circuit of mitochondrial respiration in intact cells controlled by aerobic ATP demand in the ROUTINE state of activity. 2[H] indicates the reduced hydrogen equivalents of CHO substrates and electron transfer to oxygen, with a variety of energy substrates from carbohydrates through glycolysis to the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) and glycerophosphate dehydrogenase complex (C<sub>GpDH</sub>), amino acid oxidation (AAO) and fatty acid oxidation (FAO through the electron transferring flavoprotein complex, C<sub>ETF</sub>). H<sup>+</sup><sub>out</sub> are protons pumped out of the matrix phase to the positive P-phase. Proton flow to the negative matrix phase (H<sup>+</sup><sub>in</sub>) drives the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP. Proton leaks dissipate energy of translocated protons from the positive P-phase to the negative N-phase (modified after [[Gnaiger 2012 MitoPathways]]).]] | ||
{{MitoPedia methods | {{MitoPedia methods | ||
|mitopedia method=Respirometry | |mitopedia method=Respirometry | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
== Related terms in Bioblast == | == Related terms in Bioblast == | ||
[[File:P.jpg |link=OXPHOS capacity]] [[OXPHOS capacity |OXPHOS]], ''P'' | [[File:P.jpg |link=OXPHOS capacity]] [[OXPHOS capacity |OXPHOS]], ''P'' | ||
Revision as of 17:19, 6 July 2014
Description
![]() In the intact cell, ROUTINE respiration in the physiological coupling state R, is controlled by cellular energy demand, energy turnover and the degree of coupling to phosphorylation (intrinsic uncoupling and pathological dyscoupling). R and growth of cells is supported by exogenous substrates in culture media. In media without energy substrates, R depends on endogenous substrates. R cannot be measured in permeabilized cells or isolated mitochondria. R is corrected for residual oxygen consumption (ROX), whereas R´ is the uncorrected apparent ROUTINE respiration or total cellular oxygen consumption of cells including ROX.
In the intact cell, ROUTINE respiration in the physiological coupling state R, is controlled by cellular energy demand, energy turnover and the degree of coupling to phosphorylation (intrinsic uncoupling and pathological dyscoupling). R and growth of cells is supported by exogenous substrates in culture media. In media without energy substrates, R depends on endogenous substrates. R cannot be measured in permeabilized cells or isolated mitochondria. R is corrected for residual oxygen consumption (ROX), whereas R´ is the uncorrected apparent ROUTINE respiration or total cellular oxygen consumption of cells including ROX.
Abbreviation: R
Reference: Gnaiger 2012 MitoPathways, Gnaiger_2008_POS
MitoPedia methods: Respirometry
MitoPedia topics: "Respiratory state" is not in the list (Enzyme, Medium, Inhibitor, Substrate and metabolite, Uncoupler, Sample preparation, Permeabilization agent, EAGLE, MitoGlobal Organizations, MitoGlobal Centres, ...) of allowed values for the "MitoPedia topic" property.
Respiratory state"Respiratory state" is not in the list (Enzyme, Medium, Inhibitor, Substrate and metabolite, Uncoupler, Sample preparation, Permeabilization agent, EAGLE, MitoGlobal Organizations, MitoGlobal Centres, ...) of allowed values for the "MitoPedia topic" property.
Why not 'basal respiration', and what about 'State 3.5'?
Basal respiration or "basal metabolic rate" is frequently used as LEAK respiration. Importantly, we have to make a clear distinction between (oligomycin-inhibited) LEAK respiration and physiologically controlled ROUTINE respiration, none of which conform to the physiological definition of basal respiration.
Related terms in Bioblast
![]() OXPHOS, P
OXPHOS, P
![]() ETS, E
ETS, E
![]() ROUTINE, R
ROUTINE, R
![]() LEAK, L
LEAK, L
 ROX, R
ROX, R
