Cecatto 2016 Abstract IOC116
| Cecatto C, Silva JC, Wajner A, Godoy KS, Ribeiro, RT, Amaral AU, Wajner M (2016) cis-4-Decenoic and decanoic acids impair mitochondrial energy, redox and Ca2+ homeostasis and induce mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening in rat brain and liver. Mitochondr Physiol Network 21.11 |
Link: Mitochondr Physiol Network 21.11
Cecatto C, Silva JC, Wajner A, Godoy KS, Ribeiro, RT, Amaral AU, Wajner M (2016)
Event: IOC116
Tissue accumulation of octanoic (OA), decanoic (DA) and cis-4-decenoic (cDA) acids, as well as their carnitine by-products, is the biochemistry hallmark of patients affected by medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) deficiency, the most common fatty acids oxidation disorder. Untreated patients present episodic encephalopathic crises and hepatomegaly with hiperammonemia, as well as muscle weakness and rhabdomyolysis that are usually manifested in catabolic crisis precipitated by metabolic stress situations, such as prolonged fasting and infections. However, the pathogenesis of tissue damage in MCAD deficiency is poorly known. Thus, we investigated the effects of OA, DA, cDA, octanoylcarnitine (OC) and decanoylcarnitine (DC) (0.25 – 0.5 mM) on important mitochondrial functions in isolated brain and liver mitochondria obtained from adolescent rats. DA and cDA increased resting respiration and diminished ADP- and CCCP-stimulated respiration and complexes II-III and IV activities in both tissues. The data indicate that these compounds behave as uncouplers and metabolic inhibitors of oxidative phosphorylation. Noteworthy, metabolic inhibition was more evident in brain as compared to liver. DA and cDA also markedly decreased mitochondrial membrane potential, NAD(P)H content and Ca2+ retention capacity in Ca2+-loaded brain and liver mitochondria. The reduction of Ca2+ retention capacity was more pronounced in liver and totally prevented by cyclosporine A and ADP, as well as by ruthenium red, demonstrating the involvement of mitochondrial permeability transition (mPT) and Ca2+. Furthermore, cDA induced lipid peroxidation in brain and liver mitochondria and increased hydrogen peroxide formation in brain, suggesting the participation of oxidative damage in cDA-induced alterations. Interestingly, OA, OC and DC did not alter the evaluated parameters, implying lower toxicity for these compounds. Our results suggest that DA and cDA, in contrast to OA and medium-chain acylcarnitines, disturb important mitochondrial functions in brain and liver by multiple mechanisms that are possibly involved in the neuropathology and liver alterations observed in MCAD deficiency. Our future perspectives are to investigate the in vitro and ex vivo effects of the major metabolites accumulating in MCAD deficiency on respiration coupled to H2O2 production, mitochondrial membrane potential and Ca2+ retention capacity in isolated mitochondria, tissue homogenates and biopsies of brain and liver, as well as permeabilized skeletal muscle fibers, using different respiratory substrates combinations.
• O2k-Network Lab: BR Porto Alegre Souza DOG
Labels: MiParea: Respiration Pathology: Other Stress:Permeability transition Organism: Rat Tissue;cell: Nervous system, Liver Preparation: Permeabilized tissue, Isolated mitochondria
Regulation: Calcium, Inhibitor, Uncoupler, Fatty acid Coupling state: LEAK, OXPHOS, ET Pathway: F, N, CIV, Other combinations
Affiliations
1-Dept Bioquímica, Inst Ciências Básicas Saúde, Univ Fed Rio Grande do Sul; 2-Serviço de Genética Médica, Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre, Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil. - cecattoc@gmail.com
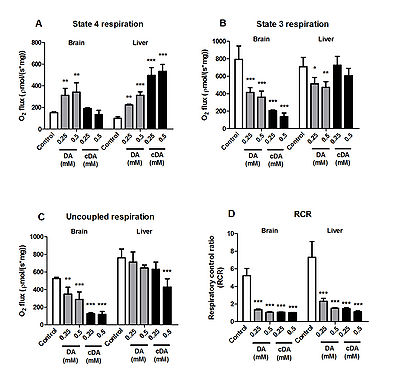
Figure 1
Figure 1.
Effects of decanoic (DA) and cis-4-decenoic (cDA) acids on respiratory parameters measured by oxygen consumption in brain and liver mitochondria. (A) Resting (state 4), (B) ADP-stimulated (state 3), (C) uncoupled (CCCP-stimulated) respiration and (D) respiratory control ratio (RCR). Glutamate plus malate (2.5 mM each) were used as substrates. Mitochondrial preparations (0.5 mg protein•mL−1) and DA or cDA (0.25–0.5 mM) were added to the incubation medium in the beginning of the assays. Controls were performed in the absence of these fatty acids. Values are means ± standard deviation for four independent experiments and are expressed as pmol O2•s−1•mg of protein−1. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, compared to controls (Duncan multiple range test).