Description
![]() Oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) is the oxidation of reduced substrates with electron transfer to oxygen, coupled to the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP and accompanied by an intrinsically uncoupled component of respiration. The OXPHOS state (P) of respiration provides a measure of OXPHOS capacity, which is frequently corrected for residual oxygen consumption (ROX).
Oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) is the oxidation of reduced substrates with electron transfer to oxygen, coupled to the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP and accompanied by an intrinsically uncoupled component of respiration. The OXPHOS state (P) of respiration provides a measure of OXPHOS capacity, which is frequently corrected for residual oxygen consumption (ROX).
Abbreviation: OXPHOS
Reference: Gnaiger 2012 MitoPathways
MitoPedia methods:
Respirometry
MitoPedia topics: "Respiratory state" is not in the list (Enzyme, Medium, Inhibitor, Substrate and metabolite, Uncoupler, Sample preparation, Permeabilization agent, EAGLE, MitoGlobal Organizations, MitoGlobal Centres, ...) of allowed values for the "MitoPedia topic" property.
Respiratory state"Respiratory state" is not in the list (Enzyme, Medium, Inhibitor, Substrate and metabolite, Uncoupler, Sample preparation, Permeabilization agent, EAGLE, MitoGlobal Organizations, MitoGlobal Centres, ...) of allowed values for the "MitoPedia topic" property.
OXPHOS
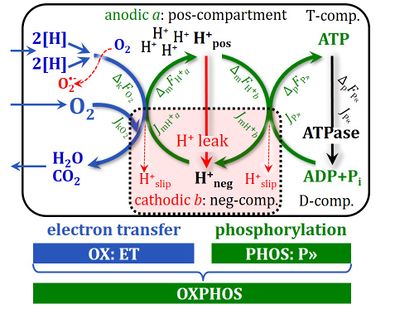
Figure: Energy transformation in coupled fluxes, J, and forces, F and Δp, of oxidative phosphorylation. 2[H] indicates the reduced hydrogen equivalents of CHO substrates and electron transfer to oxygen. JH+out is coupled output flux. Proton leaks dissipate energy of translocated protons from low pH in the positive P-phase to the negative N-phase (from Gnaiger 2012).
Related terms in Bioblast
 ROX, R
ROX, R
![]() LEAK, L
LEAK, L
![]() ROUTINE, R
ROUTINE, R
![]() ETS, E
ETS, E