Talk:Malate: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Optimum malate concentration in SUIT protocols == | |||
: '''A MiPNet publication prepared by Krumschnabel G, Heidler J, Laner V, Kotb IA, Salin K, Hand SC, Ali SS, Gnaiger E et al.''' | |||
Some representative examples are | The type and concentration of respiratory substrates is important for the design of substrate-uncoupler-inhibitor titration (SUIT) protocols. | ||
0.5 mM malate saturates CI linked respiration in combination with pyruvate and/or glutamate, whereas 2 mM malate inhibits CII linked (succinate+rotenone) and CI+II linked respiration, as shown in mouse heart (collaboration with the group of [[ET Giza Ali SS|Sameh Ali]]), mouse brain homogenate, beef heart mitochondria, human permeabilized skeletal muscle fibres, dog permeabilized skeletal muscle fibers ([http://www.oroboros.at/?IOC84_Alaska IOC84]), brine shrimp embryo (''Artemia franciscana'') mitochondria (collaboration with [[US LA Baton Rouge Hand SC|Steve Hand]]), fish liver and heart homogenates ([http://www.oroboros.at/?IOC80_schroecken#c3877| post IOC80 training course]). | |||
Some representative examples are presented here. | |||
Revision as of 06:26, 26 February 2014
Optimum malate concentration in SUIT protocols
- A MiPNet publication prepared by Krumschnabel G, Heidler J, Laner V, Kotb IA, Salin K, Hand SC, Ali SS, Gnaiger E et al.
The type and concentration of respiratory substrates is important for the design of substrate-uncoupler-inhibitor titration (SUIT) protocols.
0.5 mM malate saturates CI linked respiration in combination with pyruvate and/or glutamate, whereas 2 mM malate inhibits CII linked (succinate+rotenone) and CI+II linked respiration, as shown in mouse heart (collaboration with the group of Sameh Ali), mouse brain homogenate, beef heart mitochondria, human permeabilized skeletal muscle fibres, dog permeabilized skeletal muscle fibers (IOC84), brine shrimp embryo (Artemia franciscana) mitochondria (collaboration with Steve Hand), fish liver and heart homogenates (post IOC80 training course).
Some representative examples are presented here.
Arctic char liver homogenate:
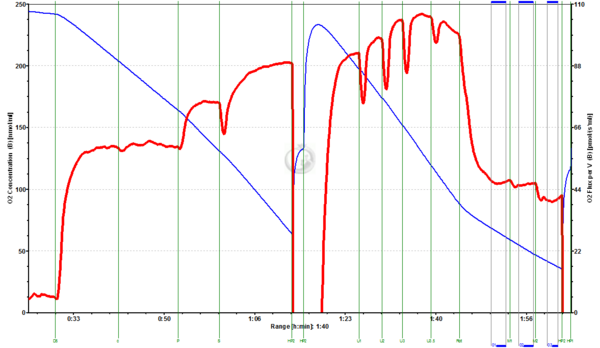
Fig.1. Arctic Char liver homogenate (3.989 mg/ml, 15°C): GM0.5+D5+c+P+S+Reox+U1+U2+U3+U3.5+Rot+M1+M2. Liver homogenate respiring at CII-linked ETS were given 1 mM Malate (M1) and 2 mM Malate (M2), which inhibited respiration by 1.1% and 13%, respectively. (Data evaluation by Karine Saline).
Arctic char heart homogenate:
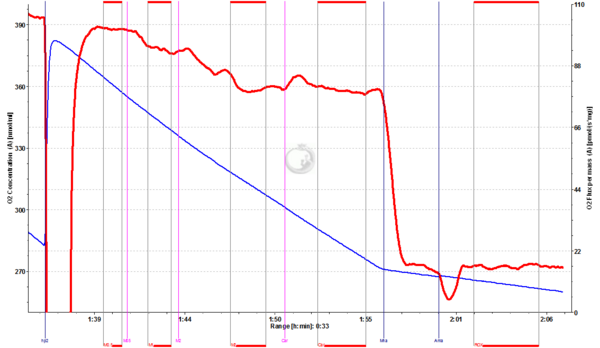
Fig.2. Arctic Char heart homogenate (1.054 mg/ml, 15°C): [G+M0.5+D5+c+P+S+Reox+U1+U2+U3+U3.5+Rot(not shown)]+M1+M2+Car+Mna+Ama. Heart homogenate respiring at CII-linked ETS was given 1 mM Malate (M1) and 2 mM Malate (M2), which inhibited respiration by 7% and 15%, respectively. Adding Carrier inhibited only 0.9%. (Data evaluation by Karine Saline).
Mouse brain homogenate:
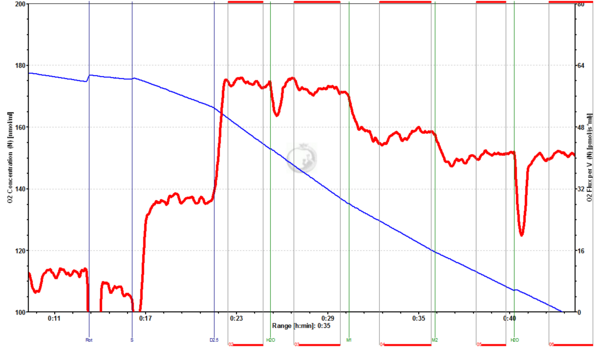
Fig.3. Mouse brain homogenate (0.9 mg/ml): Rot+S+D2.5+Car1+M1+M2+Car2. Addition of the carrier water (Car1, Car2) had no significant impact on CII-linked OXPHOS (inhibition by 2.2% and -0.2%), whereas the addition of 1 mM Malate (M1) and 2 mM Malate (M2) inhibited respiration by 21% and 11%, respectively.(Experiment and data evaluation by Kotb IA)
Beef heart mitochondria:
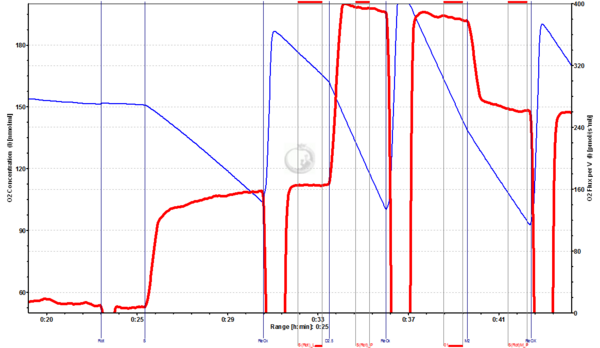
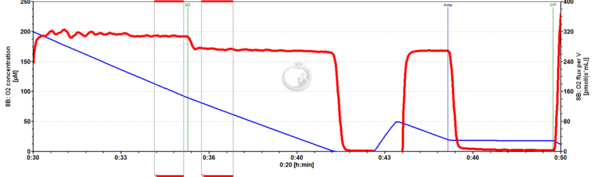
Fig.4. Beef heart mitochondria: Rot+S+D2.5+M2. Beef heat mitochondria respiring at CII-linked OXPHOS were given 2 mM Malate (M2), which inhibited respiration by 31%.
Brine shrimp embryo mitochondria:
Fig.5. Brine shrimp embryo mitochondria: [Rot+S+D2.5+cyt c+ U+M0.5 (not shown)]+M2+Ama. Brine shrimp embryo mitochondria respiring at CII-linked ETS with 0.5 mM Malate were given 2 mM Malate (M2), which inhibited respiration by 12%. (Experiment by Steve Hand).