Description
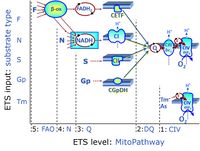
Categories of SUIT protocols group SUIT protocols according to all substrate types involved in a protocol (F, N, S, Gp), independent of the sequence of titrations of substrates and inhibitors which define the Electron-transfer-pathway states. The N-type substrates are listed in parentheses, independent of the sequence of titrations. ROX states may or may not be included in a SUIT protocol, which does not change its category. Similarly, the CIV assay may or may not be added at the end of a SUIT protocol, without effect on the category of a SUIT protocol.
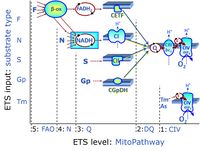
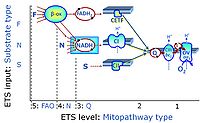
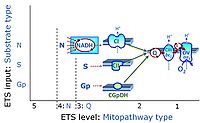
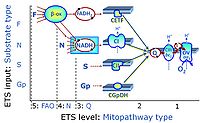
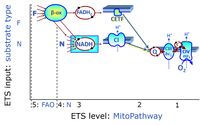
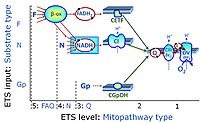
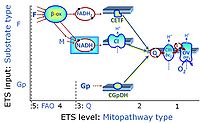
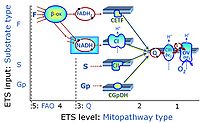
- F - ET-pathway-level 5: FADH2-linked substrates (FAO) with obligatory support by the N-linked pathway.
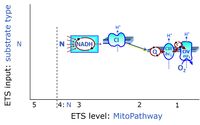
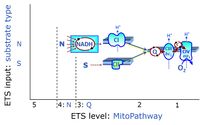
- N - ET-pathway-level 4: NADH-linked substrates (CI-linked).
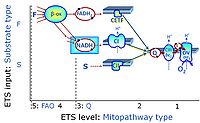
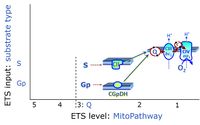
- S - ET-pathway-level 3: Succinate (CII-linked).
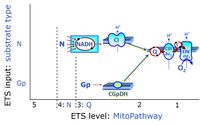
- Gp - ET-pathway-level 3: Glycerophosphate (CGpDH-linked).
- Y(X)- In the SUIT general protocols Y makes reference to the ET-pathway state and X to the combination os substrates added for the corresponding pathway.
Abbreviation: SUIT-catg
Reference: MiPNet21.06 SUIT RP
MitoPedia concepts:
SUIT concept
Categories of SUIT protocols and ET-pathway control states
| Gnaiger E (2017) Categories of SUIT protocols and ETS pathway control states. MiPNet 2017-03-12; original 2016-03-20; edited 2016-08-21. |
Abstract: The complexity of SUIT protocols is primarily determined by the large number of Electron transfer-pathway states and fuel substrates involved, compared to only three well defined coupling-control states. Whereas the SUIT protocol names specify all sequential steps in a SUIT protocol, the categories of SUIT protocols reduce this diversity to a list of substrate types involved.
• O2k-Network Lab: AT Innsbruck Oroboros
Labels: MiParea: Instruments;methods
Pathway: F, N, S, Gp, CIV, NS, Other combinations, ROX
HRR: Theory
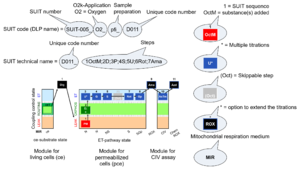
Towards a library of SUIT protocols
- At the present stage of development of the Library of SUIT protocols as part of the MitoFit Quality Control System, the substrate types linked to five ET-pathway types are considered.
- F-junction on the pathway level of converging FADH2- and NADH-linked dehydrogenases, including beta-oxidationthe and segments of the TCA cycle.
- N-junction on the pathway level of NADH-linked dehydrogenases, including the TCA cycle.
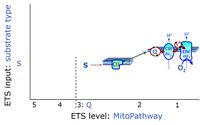
- Q-junction on the pathway level of electron transfer complexes converging at the Q-junction (S and Gp).
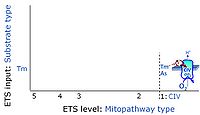
- Tm on the single step level of cytochrome c oxidase (CIV), the terminal step in the aerobic electron transfer-pathway. Tm can be included or excluded at the end of a SUIT protocol. To simplify the categorization, Tm is not considered in this system of SUIT protocols.
- At the present stage of development of the Library of SUIT protocols as part of the MitoFit Quality Control System, the substrate types linked to five ET-pathway types are considered.
Single pathway type
ET-pathway-level 1: CIV
ET-pathway-level 3: S, CII-pathway to Q
ET-pathway-level 3: Gp, CGpDH-pathway to Q
ET-pathway-level 4: N, N-junction or CI-pathway to Q
ET-pathway-level 5: F, FAO, F-junction, CETF- supported by CI-pathway to Q
Multiple ET-pathway with FNSGp
Multiple ET pathways with NS
NS
FNS
NSGp
FNSGp
Multiple ET pathways with N (without S)
FN
NGp
FNGp
Multiple ET pathways without N
- Addition of malate alone (M without P or G) is not considered as substrate type N. However, high mt-malic enzyme activity requires a change of this concept, when M alone represents an ET-pathway ccompetent substrate state. Low concentration of M may be used to support FAO, whereas a higher concentration of M may be required for N-junction respiratory capacity to override FAO capacity; this needs corresponding kinetic analyses (SUIT test protocols).