Description
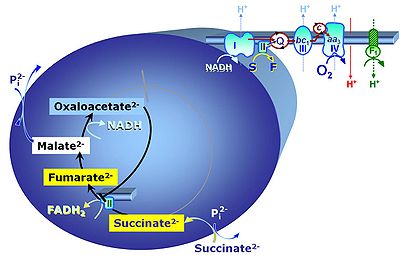
Succinic acid, C4H6O4, (butanedioic acid) is a dicarboxylic acid which occurs under physiological conditions as the anion succinate2-, S, with pKa1 = 4.2 and pKa2 = 5.6. Succinate is formed in the TCA cycle, and is a substrate of CII, reacting to fumarate and feeding electrons into the Q-junction. Succinate (CII-linked) and NADH (CI-linked) provide convergent electron entries into the Q-junction. Succinate is transported across the inner mt-membrane by the dicarboxylate carrier. The plasma membrane of many cell types is impermeable for succinate (but see Zhunussova 2015 Am J Cancer Res for an exception). Incubation of mt-preparations by succinate alone may lead to accumulation of oxaloacetate, which is a potent inhibitor of Complex II (compare Succinate and rotenone). High activities of mt-Malic enzyme (mtME) prevent accumulation of oxaloacetate in incubations with succinate without rotenone.
Abbreviation: S
Reference: Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways, Tretter 2016 Biochim Biophys Acta
Application in HRR
- S: Succinate (Sodium succinate dibasic hexahydrate; C4H404Na2 * 6H2O), Sigma-Aldrich: S2378, store at RT, CAS: 6106-21-4, M = 270.1 g·mol-1
- In the absence of CI-linked substrates, add the CI-inhibitor rotenone before addition of succinate, to avoid accumulation of oxaloacetate with subsequent inhibition of succinate dehydrogenase. See: Succinate and rotenone.
- When keeping the succinate stock solution on ice, check for complete solubilization of succinate and warm the stock solution in your hands if necessary.
- Preparation of 1 M stock solution:
- Weight 1.3505 g of succinate and dissolve in 3 mL H2O;
- Check pH and adjust to 7.0 if necessary with 1 M HCl (about 65 µL will be needed);
- Transfer to 5 mL volumetric glass flask and adjust the final volume to 5 mL;
- Divide into 0.5 mL portions;
- Store frozen at -20 °C.
- » O2k manual titrations MiPNet09.12 O2k-Titrations
- Titration volume (2-mL O2k-chamber): 20 µL using a 50 µL Hamilton syringe.
- Titration volume (0.5-mL O2k-chamber): 5 µL using a 25 µL Hamilton syringe
- Final concentration: 10 mM. Note: The concentration of succinate may be increased up to 50 mM after rotenone to compensate for the inhibitory effect of malate.
SUITbrowser question: Succinate pathway
- The SUITbrowser can be used to find the best SUIT protocols to analyze the succinate pathway, among other research questions.
MitoPedia topics:
Substrate and metabolite