Difference between revisions of "Magnesium Green"
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
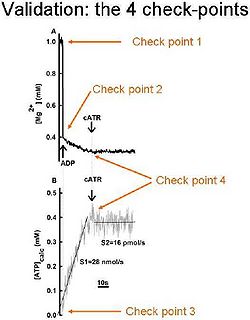
Validation of the technique: | '''Validation of the technique:''' | ||
In order be sure that the calibrated MgG signal is converted correctly to ADP-ATP exchange rate, the following 4 check-points should be sought: | In order be sure that the calibrated MgG signal is converted correctly to ADP-ATP exchange rate, the following 4 check-points should be sought: | ||
[[Image:Mg green checkpoints.jpg| 250px| left]] | |||
# <nowiki>After calibration of the MgG signal to [Mg2+], </nowiki><nowiki>the initial [Mg2+]f value </nowiki>must be equal to that added in the cuvette by the experimenter; (i.e. did you add 1 mM MgCl2 in the cuvette? Then your calibrated MgG signal must start from 1 mM free Mg2+). | # <nowiki>After calibration of the MgG signal to [Mg2+], </nowiki><nowiki>the initial [Mg2+]f value </nowiki>must be equal to that added in the cuvette by the experimenter; (i.e. did you add 1 mM MgCl2 in the cuvette? Then your calibrated MgG signal must start from 1 mM free Mg2+). | ||
| Line 26: | Line 28: | ||
# The ADP-ATP exchange rate must be completely sensitive to carboxyatractyloside, a specific blocker of the ANT. | # The ADP-ATP exchange rate must be completely sensitive to carboxyatractyloside, a specific blocker of the ANT. | ||
<nowiki>[1] Chinopoulos C, Vajda S, Csanady L, Mandi M, Mathe K, & Adam-Vizi V (2009) A novel kinetic assay of mitochondrial ATP-ADP exchange rate mediated by the ANT. Biophys. J., 96, 2490-2504.</nowiki> | <nowiki>[1] Chinopoulos C, Vajda S, Csanady L, Mandi M, Mathe K, & Adam-Vizi V (2009) A novel kinetic assay of mitochondrial ATP-ADP exchange rate mediated by the ANT. Biophys. J., 96, 2490-2504.</nowiki> | ||
Revision as of 13:24, 26 March 2012
Description
Magnesium green belongs to the extrinsic fluorophores applied for measurement of ATP production, based on different dissociation constants for ADP and ATP.
MitoPedia methods:
Fluorometry
Use of Magnesium Green 5N hexapotassium salt to measure ADP-ATP exchange rates
Application or Technique: Online fluorescence measurement of ADP-ATP exchange
[Mg2+]f determination from Magnesium Green fluorescence in the extramitochondrial volume of isolated mitochondria and conversion to ADP-ATP exchange rate: Add mitochondria to 2 ml of an incubation medium of your choice. Including the adenylate kinase inhibitor Ap5A into the medium is essential; Mg2+, which is present in the assay medium, activates adenylate kinase. Ap5A is a potent inhibitor of adenylate kinase. Magnesium Green (MgG) fluorescence can be recorded in a fluorimeter, using 506 and 530 nm excitation and emission wavelengths, respectively. MgG exhibits an extremely high quantum yield (EM[MgG]=75,000 M-1*cm-1). At the end of each experiment, minimum fluorescence (Fmin) can be measured after addition of 4 mM EDTA, followed by the recording of maximum fluorescence (Fmax) elicited by addition of 20 mM MgCl2. Free Mg2+ concentration (Mg2+f) is calculated from the equation: Mg2+f =(Kd(F-Fmin)/(Fmax-F))-0.055 mM, assuming a Kd of 0.9 mM for the MgG-Mg2+ complex. The correction term -0.055 mM is empirical, and possibly reflects chelation of other ions by EDTA that have an affinity for MgG, and alter its fluorescence. This term is needed to obtain a reliable Mg2+ estimate, as determined from calibration experiments using solutions with known, stepwise increasing, Mg2+ concentrations. ADP-ATP exchange rate is estimated using the recently described method by our laboratory [1], exploiting the differential affinity of ADP and ATP to Mg2+. The rate of ATP appearing in the medium following addition of ADP to energized mitochondria (or vice versa in case of de-energized mitochondria), is calculated from the measured rate of change in free extramitochondrial [Mg2+] using standard binding equations. The assay is designed such that the ANT is the sole mediator of changes in [Mg2+] in the extramitochondrial volume, as a result of ADP-ATP exchange [1]. For the calculation of [ATP] or [ADP] from free [Mg2+], the apparent Kd values should be estimated as described in [1].
Validation of the technique:
In order be sure that the calibrated MgG signal is converted correctly to ADP-ATP exchange rate, the following 4 check-points should be sought:
- After calibration of the MgG signal to [Mg2+], the initial [Mg2+]f value must be equal to that added in the cuvette by the experimenter; (i.e. did you add 1 mM MgCl2 in the cuvette? Then your calibrated MgG signal must start from 1 mM free Mg2+).
- After addition of ADP (or ATP) to the medium, the [Mg2+]f value must drop to the expected level, after estimating the Kd of ADP (or ATP) for Mg2+; (i.e. if you estimated Kd of ADP for Mg2+ as 0.906 mM, the addition of 2 mM ADP to 1 mM Mg2+ leads to a free Mg2+ of 0.3939 mM).
- After conversion on the calibrated [Mg2+]f to ADP, ATP level must start from “0”, if no ATP was already present in the medium, prior to adding ADP to mitochondria.
- The ADP-ATP exchange rate must be completely sensitive to carboxyatractyloside, a specific blocker of the ANT.
[1] Chinopoulos C, Vajda S, Csanady L, Mandi M, Mathe K, & Adam-Vizi V (2009) A novel kinetic assay of mitochondrial ATP-ADP exchange rate mediated by the ANT. Biophys. J., 96, 2490-2504.