Template:SUIT-002
From Bioblast
Revision as of 14:44, 11 January 2019 by Gnaiger Erich (talk | contribs)
| Step | State | Pathway | Q-junction | Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
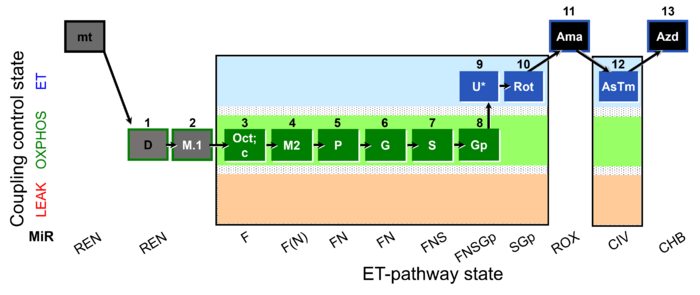
| 1D | ROX | ADP is added to stimulate consumption of endogenous fuel-substrates.
Rox is the residual oxygen consumption in the ROX state, due to oxidative side reactions, estimated either after inhibition of CIII (e.g. antimycin A, myxothiazol), CIV (e.g. Cyanide) or in the absence of endogenous fuel-substrates. Rox is subtracted from oxygen flux as a baseline for all respiratory states, to obtain mitochondrial respiration. | ||
| 2M.1 | ||||
| 3Oct | OctP | (F) | FAO | Respiratory stimulation of the FAO-pathway, F, by fatty acid, FA, in the presence of malate, M. Malate is a type N substrate (N), required for the F-pathway. The FA concentration has to be optimized to saturate the F-pathway, without inhibiting or uncoupling respiration. |
| 3c | OctMcP | F | FAO | Respiratory stimulation of the FAO-pathway, F, by fatty acid, FA, in the presence of malate, M. Malate is a type N substrate (N), required for the F-pathway. The FA concentration has to be optimized to saturate the F-pathway, without inhibiting or uncoupling respiration. OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state. Addition of cytochrome c yields a test for integrity of the mtOM (cytochrome c control efficiency). Stimulation by added cytochrome c would indicate an injury of the mtOM and limitation of respiration in the preceding state without added c due to loss of cytochrome c. Typically, cytochrome c is added immediately after the earliest ADP-activation step (OXPHOS capacity P with saturating [ADP]). |
| 4M2 | OctMP | F | FAO | |
| 5P | OctPMP | FN | FAO&CI | |
| 6G | OctPGMP | FN | FAO&CI | |
| 7S | OctPGMSP | FNS | FAO&CI&II | |
| 8Gp | OctPGMSGpP | FNSGp | FAO&CI&II&GpDH | |
| 9U | OctPGMSGpE | FNSGp | FAO&CI&II&GpDH | |
| 10Rot | SGpE | SGp | CII&GpDH | |
| 11Ama | ROX |
| Step | Respiratory state | Pathway control | ET-Complex | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ## AsTm | AsTmE | CIV | CIV | |
| ## Azd | CHB |