Difference between revisions of "Template:SUIT-003 ce1;ce2;ce3"
(Created page with "right|190px|link=http://www.bioblast.at/index.php/MitoPedia:_SUIT |MitoPedia: SUIT == Steps and respiratory states == File:Ce1;ce2(Omy);ce3U;ce4Ro...") |
|||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
| ce1;ce2Omy;ce3U;ce4* | | ce1;ce2Omy;ce3U;ce4* | ||
{{Template:SUIT ROX}} | *{{Template:SUIT Rot}} | ||
*{{Template:SUIT ROX}} | |||
*The addition of [[rotenone]] or [[Antimycin A]] will depend on the experimental question to resolve. | |||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 12:50, 21 January 2019
Steps and respiratory states
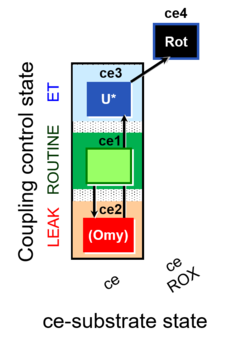
| Step | State | Pathway | Q-junction | Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M)
ROUTINE respiration in the physiological coupling state R. Externally added permeable substrates could contribute to this respiratory state. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ce1 | ROUTINE | ce1
ROUTINE respiration in the physiological coupling state R. Externally added permeable substrates could contribute to this respiratory state. | ||
| ce2(Omy) | L | ce1;ce2Omy
| ||
| ce3U | E | ce1;ce2Omy;ce3U
Uncoupler titration (avoiding inhibition by high uncoupler concentrations) to obtain electron transfer (ET) capacity E (noncoupled ET-state). Test for limitation of OXPHOS capacity P by the phosphorylation system (ANT, ATP synthase, phosphate transporter) relative to ET capacity E in mt-preparations: E-P control efficiency and E-L coupling efficiency. In living cells: E-R control efficiency and E-L coupling efficiency. Noncoupled electron transfer state, ET state, with ET capacity E.
| ||
| ce4* | ROX | ce1;ce2Omy;ce3U;ce4*
|