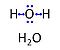Difference between revisions of "Water"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|abbr=H<sub>2</sub>O | |abbr=H<sub>2</sub>O | ||
|description=[[File:H2O.jpg|left|60px|Water]] | |description=[[File:H2O.jpg|left|60px|Water]] | ||
'''Water''', H<sub>2</sub>O, is widely used in the laboratory, particularly as a solvent and cleaning agent. Chemically pure water is | '''Water''', H<sub>2</sub>O, is widely used in the laboratory, particularly as a solvent and cleaning agent. Chemically pure water is prepared in various grades of purification: double distilled water (ddH<sub>2</sub>O) versus distilled water (dH<sub>2</sub>O or [[aqua destillata]], a.d.) and deionized or demineralized water (diH<sub>2</sub>O) with various combination purification methods. When H<sub>2</sub>O is mentioned without further specification in published protocols, it is frequently assumed that the standards of each laboratory are applied as to the quality of purified water. Purification is not only to be controlled with respect to salt content and corresponding electrical conductivity (ultra-pure water: 5.5 μS/m due to H<sup>+</sup> and OH<sup>-</sup> ions), but also in terms of microbial contamination. | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{MitoPedia methods}} | {{MitoPedia methods}} | ||
Latest revision as of 10:40, 18 February 2016
Description
Water, H2O, is widely used in the laboratory, particularly as a solvent and cleaning agent. Chemically pure water is prepared in various grades of purification: double distilled water (ddH2O) versus distilled water (dH2O or aqua destillata, a.d.) and deionized or demineralized water (diH2O) with various combination purification methods. When H2O is mentioned without further specification in published protocols, it is frequently assumed that the standards of each laboratory are applied as to the quality of purified water. Purification is not only to be controlled with respect to salt content and corresponding electrical conductivity (ultra-pure water: 5.5 μS/m due to H+ and OH- ions), but also in terms of microbial contamination.
Abbreviation: H2O
MitoPedia topics: Media for respirometry, Substrate and metabolite