Description
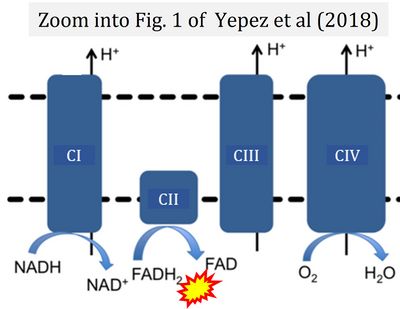
Flavin adenine dinucleotide, FAD and FADH2, is an oxidation-reduction prosthetic group (redox cofactor; compare NADH). FMN and FAD are the prosthetic groups of flavoproteins (flavin dehydrogenases). Type F substrates (fatty acids) generate FADH2, the substrate of electron transferring flavoprotein (CETF). Thus FADH2 forms a junction or funnel of electron transfer to CETF, the F-junction (compare N-junction, Q-junction), in the F-pathway control state. In contrast, FADH2 is not the substrate but the internal product of succinate dehydrogenase (CII). FAD is the oxidized (quinone) form, which is reduced to FADH2 (hydroquinone form) by accepting two electrons and two protons.
Abbreviation: FAD, FADH2
FADH2 and CII
- A commonly found error requires correction. For clarification, see page 48 in Gnaiger (2020)
- Gnaiger E (2023) Complex II ambiguities ― FADH2 in the electron transfer system. MitoFit Preprints 2023.3.v3. https://doi.org/10.26124/mitofit:2023-0003.v3
MitoPedia topics:
Substrate and metabolite
Labels:
MitoPedia:FAT4BRAIN