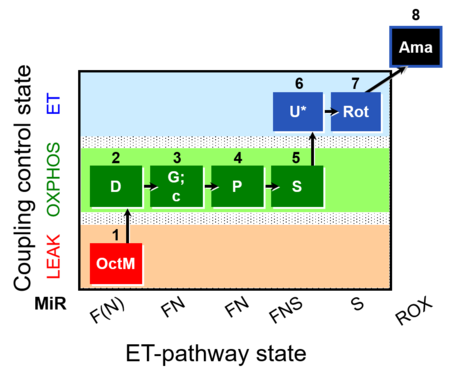
| Step
|
State
|
Pathway
|
Q-junction
|
Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M)
|
| 1OctM
|
OctML
|
F(N)
|
CETF
|
1OctM
- Respiratory stimulation of the FAO-pathway, F, by fatty acid, FA, in the presence of malate, M. Malate is a type N substrate (N), required for the F-pathway. The FA concentration has to be optimized to saturate the F-pathway, without inhibiting or uncoupling respiration.
- Non-phosphorylating resting state (LEAK state); LEAK respiration L(n) in the absence of ADP, ATP, AMP (no adenylates).
|
| 2D
|
OctMP
|
F(N)
|
CETF
|
1OctM;2D
- Respiratory stimulation of the FAO-pathway, F, by fatty acid, FA, in the presence of malate, M. Malate is a type N substrate (N), required for the F-pathway. The FA concentration has to be optimized to saturate the F-pathway, without inhibiting or uncoupling respiration.
- OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state.
|
| 3G
|
OctGMP
|
FN
|
CETF&CI
|
1OctM;2D;3G
- Respiratory stimulation of the FAO-pathway, F, by fatty acid, FA, in the presence of malate, M. Malate is a type N substrate (N), required for the F-pathway. The FA concentration has to be optimized to saturate the F-pathway, without inhibiting or uncoupling respiration. & NADH-linked substrates (type N-pathway to Q).
- Respiratory stimulation by simultaneous action of the F-pathway and N-pathway with convergent electron flow in the FN-pathway for evaluation of an additive or inhibitory effect of F.
- OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state.
|
| 3c
|
OctGMcP
|
FN
|
CETF&CI
|
1OctM;2D;3G;3c
- Respiratory stimulation by simultaneous action of the F-pathway and N-pathway with convergent electron flow in the FN-pathway for evaluation of an additive or inhibitory effect of F.
- Addition of cytochrome c yields a test for integrity of the mtOM (cytochrome c control efficiency). Stimulation by added cytochrome c would indicate an injury of the mtOM and limitation of respiration in the preceding state without added c due to loss of cytochrome c. Typically, cytochrome c is added immediately after the earliest ADP-activation step (OXPHOS capacity P with saturating [ADP]).
- OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state.
|
| 4P
|
OctPGMP
|
FN
|
CETF&CI
|
1OctM;2D;3G;3c;4P
- Respiratory stimulation of the FAO-pathway, F, by fatty acid, FA, in the presence of malate, M. Malate is a type N substrate (N), required for the F-pathway. The FA concentration has to be optimized to saturate the F-pathway, without inhibiting or uncoupling respiration. & NADH-linked substrates (type N-pathway to Q).
- Respiratory stimulation by simultaneous action of the F-pathway and N-pathway with convergent electron flow in the FN-pathway for evaluation of an additive or inhibitory effect of F.
- OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state.
|
| 5S
|
OctPGMSP
|
FNS
|
CETF&CI&II
|
1OctM;2D;3G;3c;4P;5S
- Respiratory stimulation of the FAO-pathway, F, by fatty acid, FA, in the presence of malate, M. Malate is a type N substrate (N), required for the F-pathway. The FA concentration has to be optimized to saturate the F-pathway, without inhibiting or uncoupling respiration. & NADH-linked substrates (type N-pathway to Q). & Succinate, S ( type S-pathway to Q).
- Respiratory stimulation by simultaneous action of the F-pathway, N-pathway, and S-pathway, with convergent electron flow in the FNS-pathway for reconstitution of TCA cycle function and additive or inhibitory effect of F.
- OXPHOS capacity P (with saturating [ADP]), active OXPHOS state.
|
| 6U
|
OctPGMSE
|
FNS
|
CETF&CI&II
|
1OctM;2D;3G;3c;4P;5S;6U
- Respiratory stimulation of the FAO-pathway, F, by fatty acid, FA, in the presence of malate, M. Malate is a type N substrate (N), required for the F-pathway. The FA concentration has to be optimized to saturate the F-pathway, without inhibiting or uncoupling respiration. & NADH-linked substrates (type N-pathway to Q). & Succinate, S ( type S-pathway to Q).
- Respiratory stimulation by simultaneous action of the F-pathway, N-pathway, and S-pathway, with convergent electron flow in the FNS-pathway for reconstitution of TCA cycle function and additive or inhibitory effect of F.
- Uncoupler titration (avoiding inhibition by high uncoupler concentrations) to obtain electron transfer (ET) capacity E (noncoupled ET-state). Test for limitation of OXPHOS capacity P by the phosphorylation system (ANT, ATP synthase, phosphate transporter) relative to ET capacity E in mt-preparations: E-P control efficiency and E-L coupling efficiency. In living cells: E-R control efficiency and E-L coupling efficiency.
- Noncoupled electron transfer state, ET state, with ET capacity E.
|
| 7Rot
|
SE
|
S
|
CII
|
1OctM;2D;3G;3c;4P;5S;6U;7Rot
|
| 8Ama
|
ROX
|
|
|
1OctM;2D;3G;3c;4P;5S;6U;7Rot;8Ama
- Rox is the residual oxygen consumption in the ROX state, due to oxidative side reactions, estimated after addition of antimycin A (inhibitor of CIII). Rox is subtracted from oxygen flux as a baseline for all respiratory states, to obtain mitochondrial respiration (mt).
|