Difference between revisions of "Magnesium Green"
Bader Helga (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
{{MitoPedia topics}} | {{MitoPedia topics}} | ||
Magnesium green<sup>TM</sup> is a registered trademark and available from Life Technologies (former: Invitrogen) in several formulations (e.g. #M3733). | Magnesium green<sup>TM</sup> is a registered trademark and available from Life Technologies (former: Invitrogen) in several formulations (e.g. #M3733). | ||
Note that while its ''K''<sub>D</sub> for magnesium is 1.0 mM, its ''K''<sub>D</sub> for calcium is 6 µM: Magnesium green binds stronger to calcium than to magnesium and cannot be used in the presence of significant concentrations of free calcium. | Note that while its ''K''<sub>D</sub> for magnesium is 1.0 mM, its ''K''<sub>D</sub> for calcium is 6 µM: Magnesium green binds stronger to calcium than to magnesium and cannot be used in the presence of significant concentrations of free calcium. Possible contaminations with transition metals should be complexed by a small (µM range) concentration of EDTA or DTPA. Please see also the [[Talk:Magnesium_green |discussion page]] (showing a Mg2+ calibration experiment). | ||
'''Measurement:''' >> [[O2k-Fluorescence LED2-Module]]. | '''Measurement:''' >> [[O2k-Fluorescence LED2-Module]]. | ||
Revision as of 13:16, 16 March 2015
Description
Magnesium green belongs to the extrinsic fluorophores applied for measurement of ATP production, based on different dissociation constants for ADP and ATP. » MiPNet article
Abbreviation: MgG
Reference: Kiss 2014 FASEB J, Pham 2014 Am J Physiol
MitoPedia methods:
Fluorometry
Magnesium greenTM is a registered trademark and available from Life Technologies (former: Invitrogen) in several formulations (e.g. #M3733).
Note that while its KD for magnesium is 1.0 mM, its KD for calcium is 6 µM: Magnesium green binds stronger to calcium than to magnesium and cannot be used in the presence of significant concentrations of free calcium. Possible contaminations with transition metals should be complexed by a small (µM range) concentration of EDTA or DTPA. Please see also the discussion page (showing a Mg2+ calibration experiment).
Measurement: >> O2k-Fluorescence LED2-Module.
O2k-Manual: >> Manual Fluorescent Magnesium Indicators.
Magnesium green and Calcium green share the same fluorophore moiety in their molecular structure. Therefore, the optical properties are very similar and the same fluorescence sensor and filter set can be used.
Use of Magnesium Green 5N hexapotassium salt to measure ADP-ATP exchange rates
| Chinopoulos C (2013) Use of Magnesium Green 5N hexapotassium salt to measure ADP-ATP exchange rates. Mitochondr Physiol Network 2013-02-14. |
Chinopoulos C (2013) MiPNet
Abstract: Edited by Fasching M.
• O2k-Network Lab: HU Budapest Chinopoulos C
Labels: MiParea: Respiration, Instruments;methods
Preparation: Isolated mitochondria
Regulation: ATP; ADP; AMP; PCr"ATP; ADP; AMP; PCr" is not in the list (Aerobic glycolysis, ADP, ATP, ATP production, AMP, Calcium, Coupling efficiency;uncoupling, Cyt c, Flux control, Inhibitor, ...) of allowed values for the "Respiration and regulation" property.
HRR: Oxygraph-2k, O2k-Fluorometer, Protocol"Protocol" is not in the list (Oxygraph-2k, TIP2k, O2k-Fluorometer, pH, NO, TPP, Ca, O2k-Spectrophotometer, O2k-Manual, O2k-Protocol, ...) of allowed values for the "Instrument and method" property.
Application of technique: Online fluorescence measurement of ADP-ATP exchange
[Mg2+]f determination from Magnesium Green (MgG) fluorescence in the extramitochondrial volume of isolated mitochondria and conversion to ADP-ATP exchange rate: Add mitochondria to 2 ml of an incubation medium of your choice. Including the adenylate kinase inhibitor Ap5A into the medium is essential; Mg2+, which is present in the assay medium, activates adenylate kinase. Ap5A is a potent inhibitor of adenylate kinase. MgG fluorescence can be recorded in a fluorometer, using 506 nm and 530 nm excitation and emission wavelengths, respectively. MgG exhibits an extremely high quantum yield (EM[MgG]=75,000 M-1*cm-1). At the end of each experiment, minimum fluorescence (Fmin) can be measured after addition of 4 mM EDTA, followed by the recording of maximum fluorescence (Fmax) elicited by addition of 20 mM MgCl2. Free Mg2+ concentration, [Mg2+]f, is calculated from the equation: [Mg2+]f = (Kd(F-Fmin)/(Fmax-F))-0.055 mM, assuming a Kd of 0.9 mM for the MgG-Mg2+ complex. The correction term -0.055 mM is empirical, and possibly reflects chelation of other ions by EDTA that have an affinity for MgG, and alter its fluorescence. This term is needed to obtain a reliable Mg2+ estimate, as determined from calibration experiments using solutions with known, stepwise increasing, Mg2+ concentrations. ADP-ATP exchange rate is estimated using the recently described method by our laboratory [1], exploiting the differential affinity of ADP and ATP to Mg2+. The rate of ATP appearing in the medium following addition of ADP to energized mitochondria (or vice versa in case of de-energized mitochondria), is calculated from the measured rate of change in free extramitochondrial [Mg2+]f using standard binding equations. The assay is designed such that the ANT is the sole mediator of changes in [Mg2+]f in the extramitochondrial volume, as a result of ADP-ATP exchange [1]. For the calculation of [ATP] or [ADP] from [Mg2+]f, the apparent Kd values should be estimated as described in [1].
Validation of the technique
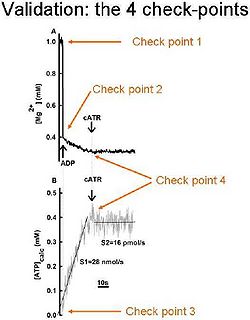
In order be sure that the calibrated MgG signal is converted correctly to ADP-ATP exchange rate, the following 4 check-points should be sought:
- After calibration of the MgG signal to [Mg2+]f, the initial [Mg2+]f value must be equal to that added in the cuvette by the experimenter; (i.e. did you add 1 mM MgCl2 in the cuvette? Then your calibrated MgG signal must start from 1 mM free Mg2+).
- After addition of ADP (or ATP) to the medium, the [Mg2+]f value must drop to the expected level, after estimating the Kd of ADP (or ATP) for Mg2+; (i.e. if you estimated Kd of ADP for Mg2+ as 0.906 mM, the addition of 2 mM ADP to 1 mM Mg2+ leads to a [Mg2+]f of 0.3939 mM).
- After conversion on the calibrated [Mg2+]f to ADP, ATP level must start from “0”, if no ATP was already present in the medium, prior to adding ADP to mitochondria.
- The ADP-ATP exchange rate must be completely sensitive to carboxyatractyloside, a specific blocker of the ANT.
[1] Chinopoulos C, Vajda S, Csanady L, Mandi M, Mathe K, Adam-Vizi V (2009) A novel kinetic assay of mitochondrial ATP-ADP exchange rate mediated by the ANT. Biophys J 96: 2490-2504.