Difference between revisions of "Glutamate"
(refined wording of pH adjustment) |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{MitoPedia | {{MitoPedia | ||
|abbr=G | |abbr=G | ||
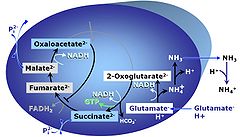
|description=[[File:Glutamic_acid.jpg|left|100px|Glutamic acid]] | |description=[[File:Glutamic_acid.jpg|left|100px|Glutamic acid]]'''Glutamic acid''', C<sub>5</sub>H<sub>9</sub>NO<sub>4</sub>, is an amino acid which occurs under physiological conditions mainly as the anion '''glutamate<sup>-</sup>, G''', with ''p''K<sub>a1</sub> = 2.1, ''p''K<sub>a2</sub> = 4.07 and ''p''K<sub>a3</sub> = 9.47. Glutamate&malate is a substrate combination supporting an N-linked pathway control state, when glutamate is transported into the mt-matrix via the [[glutamate-aspartate carrier]] and reacts with [[oxaloacetate]] in the transaminase reaction to form aspartate and [[oxoglutarate]]. Glutamate as the sole substrate is transported by the electroneutral glutamate<sup>-</sup>/OH<sup>-</sup> exchanger, and is oxidized in the mitochondrial matrix by [[glutamate dehydrogenase]] to α-ketoglutarate ([[oxoglutarate|2-oxoglutarate]]), representing the [[glutamate-anaplerotic pathway control state]]. Ammonia (the byproduct of the reaction) passes freely through the mitochondrial membrane. | ||
'''Glutamic acid''', C<sub>5</sub>H<sub>9</sub>NO<sub>4</sub>, is an amino acid which occurs under physiological conditions mainly as the anion '''glutamate<sup>-</sup>, G''', with ''p''K<sub>a1</sub> = 2.1, ''p''K<sub>a2</sub> = 4.07 and ''p''K<sub>a3</sub> = 9.47. Glutamate&malate is a substrate combination supporting an N-linked pathway control state, when glutamate is transported into the mt-matrix via the [[glutamate-aspartate carrier]] and reacts with [[oxaloacetate]] in the transaminase reaction to form aspartate and [[oxoglutarate]]. Glutamate as the sole substrate is transported by the electroneutral glutamate<sup>-</sup>/OH<sup>-</sup> exchanger, and is oxidized in the mitochondrial matrix by [[glutamate dehydrogenase]] to α-ketoglutarate ([[oxoglutarate | 2-oxoglutarate]]), representing the [[glutamate-anaplerotic pathway control state]]. Ammonia (the byproduct of the reaction) passes freely through the mitochondrial membrane. | |info=[[Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways]] | ||
|info=[[Gnaiger | |||
}} | }} | ||
[[File:G.jpg|right|240px|link=Glutamate-anaplerotic pathway control state|G]] | [[File:G.jpg|right|240px|link=Glutamate-anaplerotic pathway control state|G]] | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
== Application in [[HRR]] == | == Application in [[HRR]] == | ||
{{Chemical_description | |||
|abbr=G | |||
|trivial name=Glutamate | |||
|complete name=L-Glutamic acid, monosodium salt hydrate | |||
|chem formula=C₅H₈NNaO₄ · xH₂O | |||
|molar mass=169.1 | |||
|vendor=Sigma-Aldrich | |||
|product number=G1626 | |||
|store at=RT | |||
|sensitivity= | |||
|cas=142-47-2 | |||
|h statements= | |||
|h info= | |||
}}<!--::: '''G: Glutamate''' (L-Glutamic acid, monosodium salt hydrate, C<sub>5</sub>H<sub>8</sub>NO<sub>4</sub>Na; contains 1 mol H<sub>2</sub>O /mol); Sigma G 1626, 100 g, store at R.T.; M = 169.1 g·mol<sup>-1</sup>)--> | |||
:::: '''Preparation of 2 M stock solution''' (dissolved in H<sub>2</sub>O) | :::: '''Preparation of 2 M stock solution''' (dissolved in H<sub>2</sub>O) | ||
::::# Weigh 1.691 g L-Glutamic acid, monosodium salt hydrate | ::::# Weigh 1.691 g L-Glutamic acid, monosodium salt hydrate. | ||
::::# Add 4 mL H<sub>2</sub>O. | ::::# Add 4 mL H<sub>2</sub>O. | ||
::::# Check pH and adjust to 7.0 if necessary with 5 M KOH (usually the pH is 7 without any adjustment); | ::::# Check pH and adjust to 7.0 if necessary with 5 M KOH (usually the pH is 7 without any adjustment); | ||
::::# Transfer to a 5 mL volumetric glass flask, adjust final volume to 5 mL and divide into 0.5 mL portions. | |||
::::# | |||
::::# Store at -20 °C. | ::::# Store at -20 °C. | ||
| Line 26: | Line 39: | ||
::::* Titration volume ('''0.5-mL O2k-chamber'''): 2.5 µL using a 10 µL Hamilton syringe | ::::* Titration volume ('''0.5-mL O2k-chamber'''): 2.5 µL using a 10 µL Hamilton syringe | ||
::::* Final concentration: 10 mM. | ::::* Final concentration: 10 mM. | ||
{{MitoPedia concepts}} | |||
{{MitoPedia methods}} | |||
{{MitoPedia O2k and high-resolution respirometry}} | |||
{{MitoPedia topics | {{MitoPedia topics | ||
|mitopedia topic=Substrate and metabolite | |mitopedia topic=Substrate and metabolite | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 09:26, 4 July 2023
Description
Glutamic acid, C5H9NO4, is an amino acid which occurs under physiological conditions mainly as the anion glutamate-, G, with pKa1 = 2.1, pKa2 = 4.07 and pKa3 = 9.47. Glutamate&malate is a substrate combination supporting an N-linked pathway control state, when glutamate is transported into the mt-matrix via the glutamate-aspartate carrier and reacts with oxaloacetate in the transaminase reaction to form aspartate and oxoglutarate. Glutamate as the sole substrate is transported by the electroneutral glutamate-/OH- exchanger, and is oxidized in the mitochondrial matrix by glutamate dehydrogenase to α-ketoglutarate (2-oxoglutarate), representing the glutamate-anaplerotic pathway control state. Ammonia (the byproduct of the reaction) passes freely through the mitochondrial membrane.
Abbreviation: G
Reference: Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways
Application in HRR
- G: Glutamate (L-Glutamic acid, monosodium salt hydrate; C₅H₈NNaO₄ · xH₂O), Sigma-Aldrich: G1626, store at RT, CAS: 142-47-2, M = 169.1 g·mol-1
- Preparation of 2 M stock solution (dissolved in H2O)
- Weigh 1.691 g L-Glutamic acid, monosodium salt hydrate.
- Add 4 mL H2O.
- Check pH and adjust to 7.0 if necessary with 5 M KOH (usually the pH is 7 without any adjustment);
- Transfer to a 5 mL volumetric glass flask, adjust final volume to 5 mL and divide into 0.5 mL portions.
- Store at -20 °C.
- » O2k manual titrations MiPNet09.12 O2k-Titrations
- Titration volume (2-mL O2k-chamber): 10 µL using a 25 µL Hamilton syringe.
- Titration volume (0.5-mL O2k-chamber): 2.5 µL using a 10 µL Hamilton syringe
- Final concentration: 10 mM.
MitoPedia topics:
Substrate and metabolite