Difference between revisions of "SUIT-008"
From Bioblast
| (22 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{MitoPedia | {{MitoPedia | ||
|abbr= | |abbr=PM+G+S_OXPHOS+Rot_ET | ||
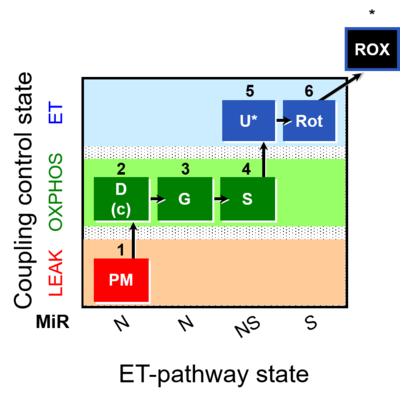
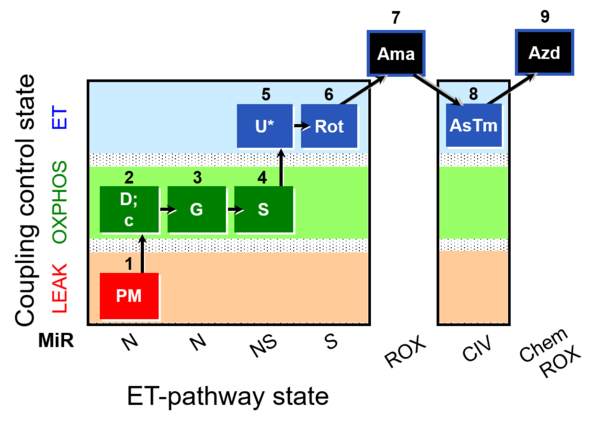
|description=[[File:1PM;2D;3G;4S;5U;6Rot.png|400px]] | |description=[[File:1PM;2D;3G;4S;5U;6Rot.png|400px]] | ||
|info='''A: Additivity between the N- and S-pathway in the Q-junction''' | |info='''A: Additivity between the N- and [[Succinate pathway control state| S-pathway]] in the Q-junction''' | ||
}} | }} | ||
::: '''[[SUIT protocol pattern]]:''' 1PM;2D;3G;4S;5U;6Rot- | |||
::: '''[[SUIT protocol pattern]]:''' | |||
The SUIT-008 protocols are designed to assess the additivity between the [[NADH_Electron_transfer-pathway_state| N-]] and [[Succinate pathway control state| S-pathway]] in the [[Q-junction]], providing a physiologically relevant estimate of maximum mitochondrial respiratory capacity. SUIT-008 also serves as a diagnostic tool for the activity of the [[glutamate dehydrogenase]] and its linked pathways, which could be relevant in some pathologies. SUIT-008 can be easily extended with the CIV assay module. | |||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
Communicated by [[Cardoso | Communicated by [[Cardoso LHD]], [[Doerrier C]], [[Gnaiger E]] (last update 2019-06-05) | ||
== Specific SUIT protocols == | == Specific SUIT protocols == | ||
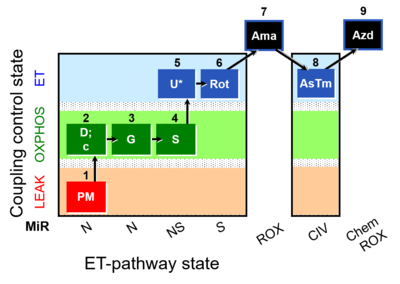
[[File:1PM;2D;2c;3G;4S;5U;6Rot;7Ama;8AsTm; | [[File:1PM;2D;2c;3G;4S;5U;6Rot;7Ama;8AsTm;9Azd.png|400px]] | ||
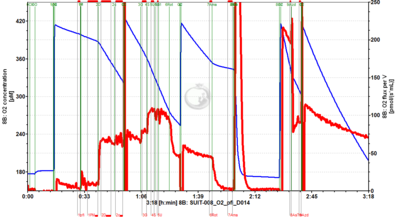
[[File:D014_O2_traces.png|400px]] | |||
* [[SUIT-008 O2 pfi D014]] for permeabilized fibers | * [[SUIT-008 O2 pfi D014]] for permeabilized fibers | ||
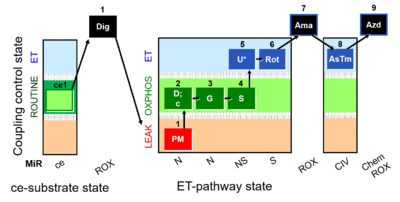
[[File:ce1;1Dig;1PM;2D;2c;3G;4S;5U;6Rot;7Ama;8AsTm; | [[File:ce1;1Dig;1PM;2D;2c;3G;4S;5U;6Rot;7Ama;8AsTm;9Azd.png|400px]] | ||
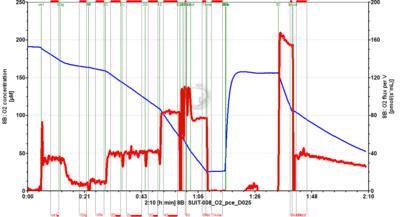
* [[SUIT-008 O2 pce D025]] for permeabilized cells | [[File:D025_O2_traces.png|400px]] | ||
* [[SUIT-008 O2 ce-pce D025]] for cells-permeabilized cells (ce-pce) | |||
[[File:1PM;2D;2c;3G;4S;5U;6Rot;7Ama;8AsTm;9Azd.png|400px]] | |||
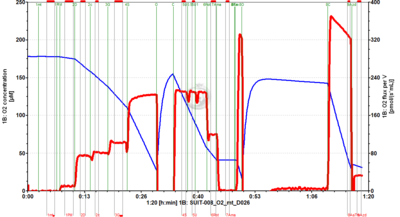
[[File:D026_O2_traces.png|400px]] | |||
* [[SUIT-008 O2 mt D026]] for isolated mitochondria and tissue homogenate | |||
{{Template:SUIT-008}} | {{Template:SUIT-008}} | ||
| Line 24: | Line 29: | ||
:::+ The presence of PGM and S establishes fully operative TCA cycle activity. | :::+ The presence of PGM and S establishes fully operative TCA cycle activity. | ||
:::+ This protocol allows to analyse the convergence of pathways at the Q-junction (N, NS, S). | :::+ This protocol allows to analyse the convergence of pathways at the Q-junction (N, NS, S). | ||
:::+ | :::+ Outer mitochondrial membrane integrity can be evaluated by the addition of cytochrome ''c'' ([[Cytochrome c control factor |cytochrome ''c'' test]]). The early addition of cytochrome ''c'' in the protocol ensures comparability of all states in case of any effect of cytochrome ''c'. | ||
:::+ GM and PM yield typically identical fluxes in human skeletal muscle fibres. However, PM is the superior alternative to GM: the fraction of the N-pathway is lower and S-pathway contribution is higher with GM compared to PM. PM, therefore, yields a more sensitive assay for the diagnosis of injuries in the N-pathway, since impairment of N-pathway capacity can be compensated partially by activation of the S-pathway. This is an advantage compared to [[SUIT-011]] for the diagnosis of N-capacity. | |||
:::+ Reasonable duration of the experiment. | :::+ Reasonable duration of the experiment. | ||
:::+ Complex IV | :::+ This protocol can be extended with the Complex IV module. | ||
::: | :::- F-pathway is not analysed. | ||
:::- For additive effect evaluation of N- and S-pathways, it has to be considered that NS<sub>''P''</sub> and NS<sub>''E''</sub> capacities can only be compared with N<sub>''P''</sub> and S<sub>''E''</sub> capacities. This is not a problem when NS<sub>''P''</sub> = NS<sub>''E''</sub> (Gnaiger 2009). In this case, it may be assumed that S<sub>''P''</sub> = S<sub>''E''</sub> (Votion et al 2012), such that NS<sub>''P''</sub> can be compared with N<sub>''P''</sub> + S<sub>''P''</sub>. [[SUIT-004]] should be chosen for the additive effect in the ET-state. | |||
:::- | |||
:::- Careful washing is required after the experiment to avoid carry-over of inhibitors and uncoupler. | :::- Careful washing is required after the experiment to avoid carry-over of inhibitors and uncoupler. | ||
== Compare SUIT protocols == | == Compare SUIT protocols == | ||
::::* [[SUIT-004]] 1PM;2D;3U;4S;5Rot- The SUIT-004 | ::::* [[SUIT-014]]: 1GM;2D;3P;4S;5U;6Rot-; similar version starting with GM, and then adding P. Used in combination with SUIT-008 in [[Lemieux_2017_Sci_Rep|Lemieux 2017]]. | ||
::::* [[SUIT-011]] 1GM;2D;3S;4U;5Rot- | ::::* [[SUIT-004]]: 1PM;2D;3U;4S;5Rot- The SUIT-004 protocols provide a quick assessment of linear coupling control (''L''- ''P''- ''E'') with NADH-linked substrates (PM) and pathway control in the ET state (N, NS, S) | ||
::::* [[SUIT-011]]: 1GM;2D;3S;4U;5Rot- The SUIT-011 protocols are designed to study physiologically relevant maximum mitochondrial respiratory capacity (OXPHOS with NS substrates) and coupling/pathway control. | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 09:41, 30 November 2023
Description
Abbreviation: PM+G+S_OXPHOS+Rot_ET
Reference: A: Additivity between the N- and S-pathway in the Q-junction
- SUIT protocol pattern: 1PM;2D;3G;4S;5U;6Rot-
The SUIT-008 protocols are designed to assess the additivity between the N- and S-pathway in the Q-junction, providing a physiologically relevant estimate of maximum mitochondrial respiratory capacity. SUIT-008 also serves as a diagnostic tool for the activity of the glutamate dehydrogenase and its linked pathways, which could be relevant in some pathologies. SUIT-008 can be easily extended with the CIV assay module.
Communicated by Cardoso LHD, Doerrier C, Gnaiger E (last update 2019-06-05)
Specific SUIT protocols
- SUIT-008 O2 pfi D014 for permeabilized fibers
- SUIT-008 O2 ce-pce D025 for cells-permeabilized cells (ce-pce)
- SUIT-008 O2 mt D026 for isolated mitochondria and tissue homogenate
Steps and respiratory states
| Step | State | Pathway | Q-junction | Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1PM | PML(n) | N | CI | 1PM
|
| 2D | PMP | N | CI | 1PM;2D
|
| 2c | PMcP | N | CI | 1PM;2D;2c
|
| 3G | PGMP | N | CI | 1PM;2D;2c;3G
|
| 4S | PGMSP | NS | CI&II | 1PM;2D;2c;3G;4S
|
| 5U | PGMSE | NS | CI&II | 1PM;2D;2c;3G;4S;5U
|
| 6Rot | SE | S | CII | 1PM;2D;2c;3G;4S;5U;6Rot
|
| 7Ama | ROX | 1PM;2D;2c;3G;4S;5U;6Rot;7Ama
|
| Step | Respiratory state | Pathway control | ET-Complex | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ## AsTm | AsTmE | CIV | CIV | |
| ## Azd | CHB |
- Bioblast links: SUIT protocols - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Coupling control
- Pathway control
- Main fuel substrates
- » Glutamate, G
- » Glycerophosphate, Gp
- » Malate, M
- » Octanoylcarnitine, Oct
- » Pyruvate, P
- » Succinate, S
- Main fuel substrates
- Glossary
Strengths and limitations
- + NS-OXPHOS capacity provides a physiologically relevant estimate of maximum mitochondrial respiratory capacity.
- + The presence of PGM and S establishes fully operative TCA cycle activity.
- + This protocol allows to analyse the convergence of pathways at the Q-junction (N, NS, S).
- + Outer mitochondrial membrane integrity can be evaluated by the addition of cytochrome c (cytochrome c test). The early addition of cytochrome c in the protocol ensures comparability of all states in case of any effect of cytochrome c'.
- + GM and PM yield typically identical fluxes in human skeletal muscle fibres. However, PM is the superior alternative to GM: the fraction of the N-pathway is lower and S-pathway contribution is higher with GM compared to PM. PM, therefore, yields a more sensitive assay for the diagnosis of injuries in the N-pathway, since impairment of N-pathway capacity can be compensated partially by activation of the S-pathway. This is an advantage compared to SUIT-011 for the diagnosis of N-capacity.
- + Reasonable duration of the experiment.
- + This protocol can be extended with the Complex IV module.
- - F-pathway is not analysed.
- - For additive effect evaluation of N- and S-pathways, it has to be considered that NSP and NSE capacities can only be compared with NP and SE capacities. This is not a problem when NSP = NSE (Gnaiger 2009). In this case, it may be assumed that SP = SE (Votion et al 2012), such that NSP can be compared with NP + SP. SUIT-004 should be chosen for the additive effect in the ET-state.
- - Careful washing is required after the experiment to avoid carry-over of inhibitors and uncoupler.
Compare SUIT protocols
- SUIT-014: 1GM;2D;3P;4S;5U;6Rot-; similar version starting with GM, and then adding P. Used in combination with SUIT-008 in Lemieux 2017.
- SUIT-004: 1PM;2D;3U;4S;5Rot- The SUIT-004 protocols provide a quick assessment of linear coupling control (L- P- E) with NADH-linked substrates (PM) and pathway control in the ET state (N, NS, S)
- SUIT-011: 1GM;2D;3S;4U;5Rot- The SUIT-011 protocols are designed to study physiologically relevant maximum mitochondrial respiratory capacity (OXPHOS with NS substrates) and coupling/pathway control.
References
| Year | Reference | Organism | Tissue;cell | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lemieux 2017 Sci Rep | 2017 | Lemieux H, Blier PU, Gnaiger E (2017) Remodeling pathway control of mitochondrial respiratory capacity by temperature in mouse heart: electron flow through the Q-junction in permeabilized fibers. Sci Rep 7:2840. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-02789-8 | Mouse | Heart |
MitoPedia concepts: MiP concept, SUIT protocol, Recommended
MitoPedia methods:
Respirometry