Semantic search
| Term | Abbreviation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| O2k-Fluo Smart-Module | The O2k-Fluo Smart-Module is an amperometric add-on module to the O2k-Respirometer, adding a new dimension to high-resolution respirometry. Optical sensors are inserted through the front window of the O2k-glass chambers, for measurement of hydrogen peroxide production (Amplex® UltraRed), ATP production (Magnesium Green™), mt-membrane potential (Safranin, TMRM), Ca2+ (Calcium Green™), and numerous other applications open for O2k-user innovation. | |
| O2k-FluoRespirometer | The Oroboros O2k-FluoRespirometer - the experimental system complete for high-resolution respirometry (HRR), including fluorometry, the TIP2k and the O2k-sV-Module allowing simultaneous monitoring of oxygen consumption together with either ROS production (AmR), mt-membrane potential (TMRM, Safranin and Rhodamine 123), Ca2+ (CaG) or ATP production (MgG). The O2k-FluoRespirometer supports all add-on O2k-Modules: O2k-TPP+ ISE-Module, O2k-pH ISE-Module, O2k-NO Amp-Module, enabling measurement of mt-membrane potential with ion sensitive electrodes (ISE for TPP+ or TPMP+) or pH. | |
| O2k-sV-Module | O2k-sV-Module |
The O2k-sV-Module is the O2k small-volume module, comprised of two Duran® glass chambers of 12 mm inner diameter specifically developed to perform high-resolution respirometry with reduced amounts of biological sample, and all the components necessary for a smaller operation volume V of 0.5 mL. The current DatLab version is included in the delivery of this revolutionary module. |
| Optics | Optics are the components that are used to relay and focus light through a spectrofluorometer or spectrophotometer. These would normally consist of lenses and/or concave mirrors. The number of such components should be kept to a minimum due to the losses of light (5-10%) that occur at each surface. | |
| PH calibration buffers | pH calibration buffers are prepared to obtain two or more defined pH values for calibration of pH electrodes and pH indicator dyes. | |
| Phosphorescence | Phosphorescence is a similar phenomenon to fluorescence. However, instead of the electron returning to its original energy state following excitation, it decays to an intermediate state (with a different spin value) where it can remain for some time (minutes or even hours) before decaying to its original state. Phosphorescence is one form of Luminescence, especially Photoluminescence. | |
| Photodiode arrays | Photodiode arrays are two dimensional assemblies of photodiodes. They are frequently used in conjunction with charge coupled devices (CCDs) for digital imaging. They can be used in combination with dispersion devices to detect wavelength dependent light intensities in a spectrofluorometer or spectrophotometer. | |
| Photodiodes | Photodiodes are photodetectors that convert incident light into a current or voltage dependent on their configuration. They have replaced photomultiplier tubes for most applications. For fluorometric measurements that do not require spectral data, a single photodiode with suitable filters can be used. Due to their larger detection area, they are more sensitive than photodiode arrays. | |
| Polyether ether ketone | PEEK | Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is a semicrystalline organic polymer thermoplastic, which is chemically very resistant, with excellent mechanical properties. PEEK is compatible with ultra-high vacuum applications, and its resistance against oxygen diffusion make it an ideal material for high-resolution respirometry (POS insulation; coating of stirrer bars; stoppers for closing the O2k-Chamber). |
| Power O2k-FluoRespirometer | Power O2k-FluoRespirometer - optional configuration as additional system for increasing output combined with the O2k-FluoRespirometer (O2k-Series H). The Power O2k-FluoRespirometer includes the TIP2k and the O2k-sV-Module, and supports all add-on O2k-Modules of the Oroboros O2k. It can be added to an existing Oroboros O2k of any O2k-Series. This application does not require an additional ISS-Integrated Suction System and O2k-Titration Set. Furthermore, the OroboPOS-Mounting Tool of the OroboPOS Service Tools can be used from the available O2k and is not included. | |
| Quenching | Quenching is the name given to any process that reduces fluorescence intensity. Molecular oxygen is a fluorescence and phosphorescence quencher for some substances – a phenomenon that has been made use of in constructing optical probes for measuring oxygen. | |
| Reactive oxygen species | ROS | Reactive oxygen species, ROS, are molecules derived from molecular oxygen, including free oxygen radicals, which are more reactive than O2. Physiologically and pathologically important ROS include superoxide, the hydroxyl radical and hydroxide ion, hydrogen peroxide and other peroxides. These are important in cell signalling, oxidative defence mechanisms and oxidative stress. |
| Resolution | Spectral resolution is a measure of the ability of an instrument to differentiate between two adjacent wavelengths. Two wavelengths are normally considered to be resolved if the minimum detector output signal (trough) between the two peaks is lower than 80 % of the maximum. The resolution of a spectrofluorometer or spectrophotometer is dependent on its bandwidth. | |
| Resorufin | Res | Resorufin is a fluorescence probe used in various biological assays. Among others, it is the product obtained in the Horseradish peroxidase-catalyzed assay using Amplex Red for the measurement of H2O2 production. |
| Rhodamine 123 | Rh123 | Rhodamine 123 (Rh123) is an extrinsic fluorophore and can be used as a probe to determine changes in mitochondrial membrane potential. Rh123 is a lipophilic cation that is accumulated by mitochondria in proportion to Δψmt. Using ethanol as the solvent, the excitation maximum is 511 nm and the emission maximum is 534 nm. The recommended excitation and emission wavelengths in PBS are 488 and 515-575 nm, respectively (Sigma-Aldrich). |
| SUIT-003 AmR ce D017 | CCP-ce S permeability test | 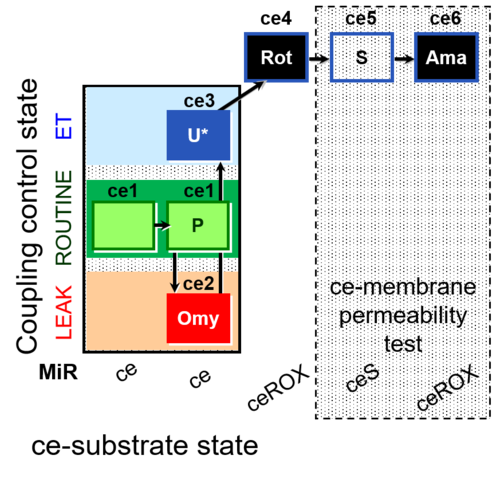 |
| SUIT-006 | CCP-mtprep | 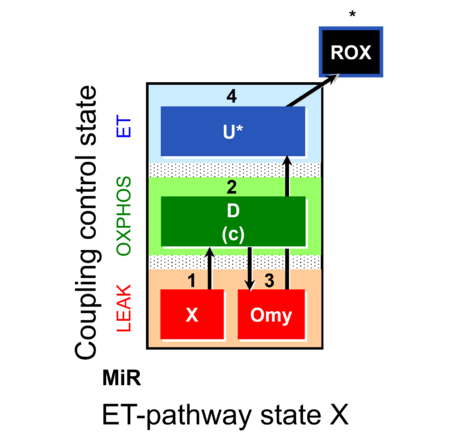 |
| SUIT-006 AmR mt D048 | CCP mt PM - AmR | 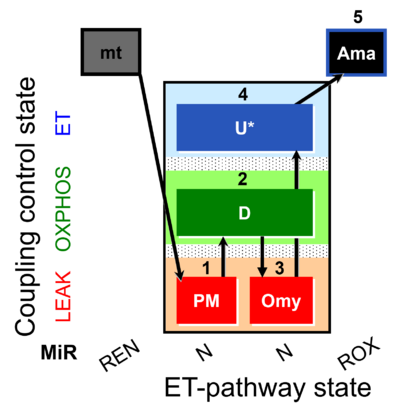 |
| SUIT-006 Fluo mt D034 | CCP mt PM - Fluo | 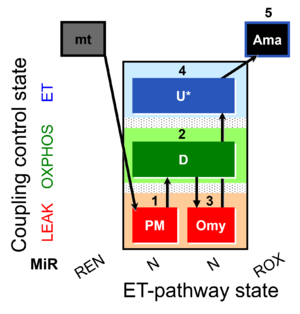 |
| SUIT-006 MgG ce-pce D085 | CCP MgG ce-pce | 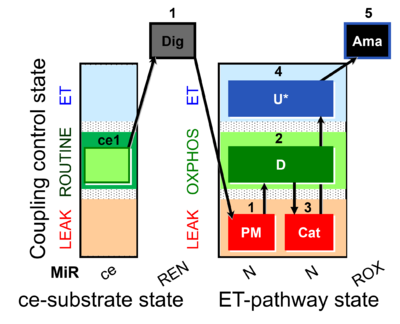 |
| SUIT-006 MgG mt D055 | CCP MgG mt | 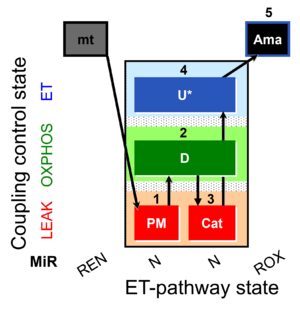 |
| SUIT-009 | 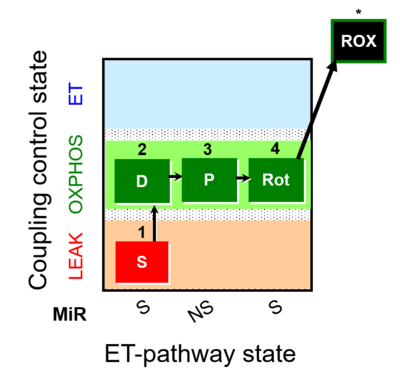 | |
| SUIT-009 AmR ce-pce D019 | H2O2 RET ce-pce S_L | 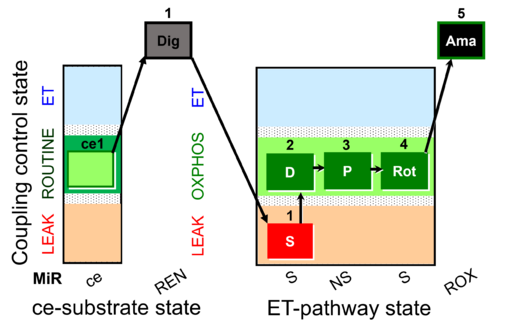 |
| SUIT-009 AmR mt D021 | H2O2 mtprep | 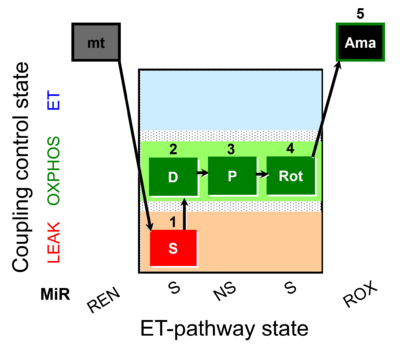 |
| SUIT-013 | ce | 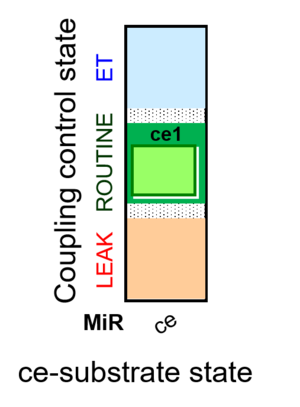 |
| SUIT-013 AmR ce D023 | O2 dependence of H2O2 production ce | 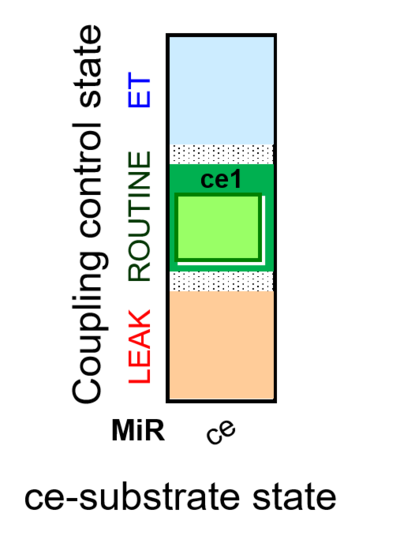 |
| SUIT-018 | O2 dependence-H2O2 | 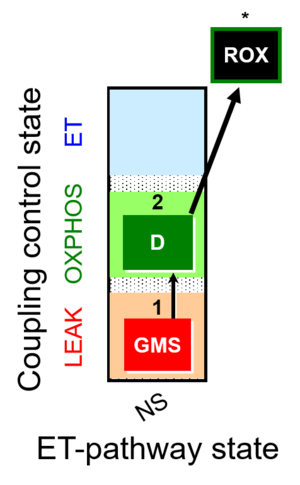 |
| SUIT-018 AmR ce-pce D068 | O2 dependence-H2O2 | 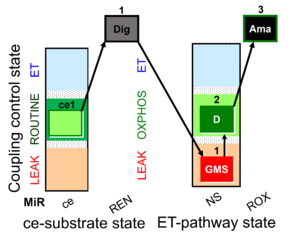 |
| SUIT-018 AmR mt D031 | O2 dependence-H2O2 | 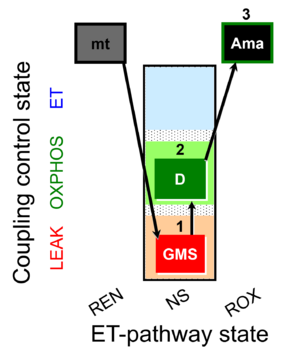 |
| SUIT-018 AmR mt D040 | NS(GM) |  |
| SUIT-018 AmR mt D041 | O2 dependence-H2O2 |  |
| SUIT-020 | PM+G+S+Rot_OXPHOS+Omy | 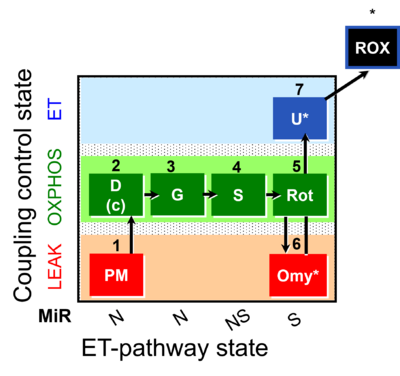 |
| SUIT-020 Fluo mt D033 | NS(PGM) | 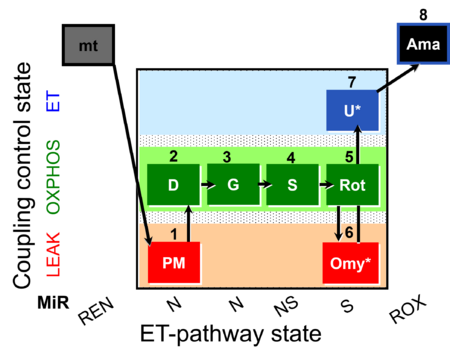 |
| SUIT-021 | OXPHOS (GM+S+Rot+Omy) | 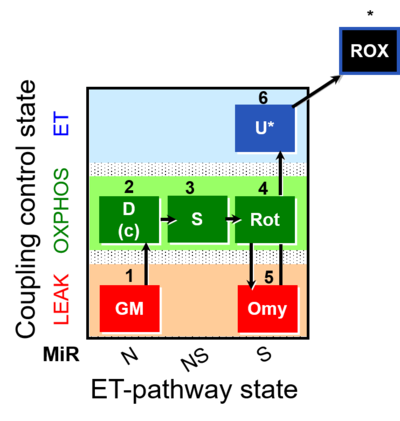 |
| SUIT-021 Fluo mt D036 | NS(GM) | 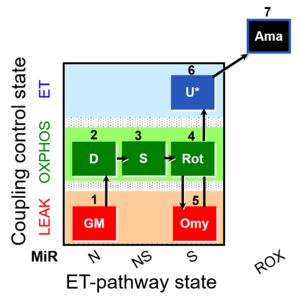 |
| SUIT-026 | RET | 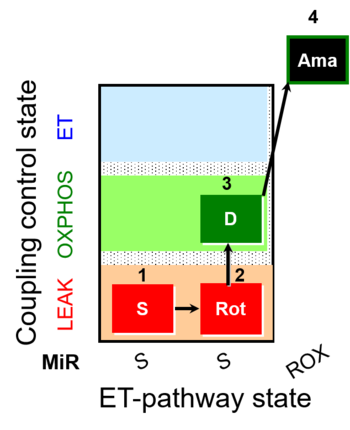 |
| SUIT-026 AmR ce-pce D087 | RET | 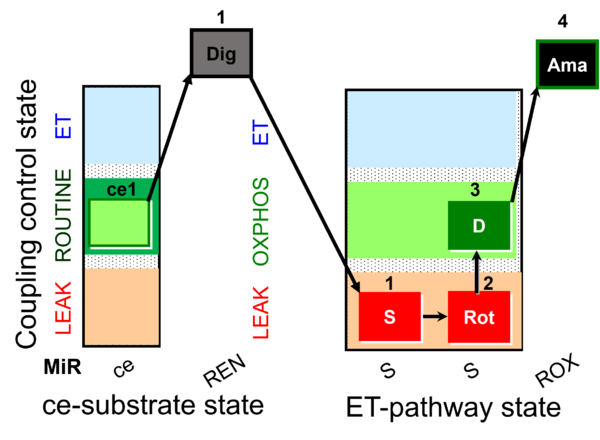 |
| SUIT-026 AmR mt D064 | RET | 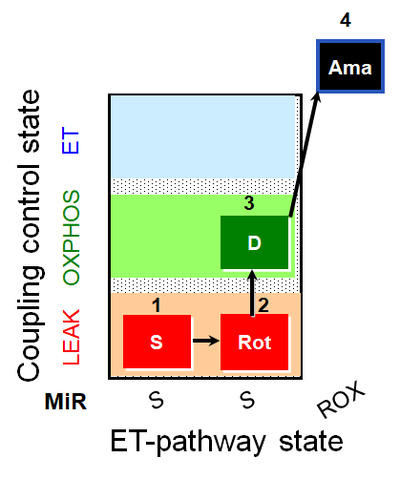 |
| SUIT-026 AmR mt D077 | RET |  |
| SUIT-026 O2 ce-pce D088 | RET (respiratory control) of SUIT-026 AmR ce-pce D087 | 400px |
| SUIT-026 O2 mt D063 | RET (respiratory control) of SUIT-026 AmR mt D064 | 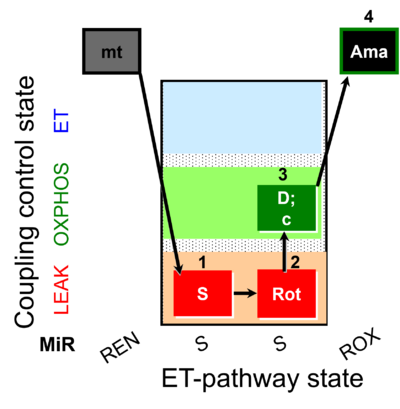 |
| SUIT-027 O2 ce-pce D065 | Malate anaplerosis | 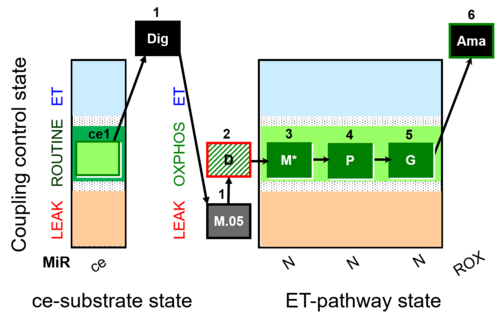 |
| SUITbrowser | Use the SUITbrowser to find the substrate-uncoupler-inhibitor-titration (SUIT) protocol most suitable for addressing your research questions. Open the SUITbrowser: http://suitbrowser.oroboros.at/ | |
| Safranin | Saf | Safranin is one of the most established dyes for measuring mitochondrial membrane potential by fluorometry. It is an extrinsic fluorophore with an excitation wavelength of 495 nm and emission wavelength of 587 nm. Safranin is a potent inhibitor of N-linked respiration and of the phosphorylation system. Synonyms: Safranin O, Safranin Y, Safranin T, Gossypimine, Cotton Red, Basic Red2 |
| Scattering | Most biological samples do not consist simply of pigments but also particles (e.g. cells, fibres, mitochondria) which scatter the incident light. The effect of scattering is an apparent increase in absorbance due to an increase in pathlength and the loss of light scattered in directions other than that of the detector. Two types of scattering are encountered. For incident light of wavelength λ, Rayleigh scattering is due to particles of diameter < λ (molecules, sub-cellular particles). The intensity of scatter light is proportional to λ4 and is predominantly backward scattering. Mie scattering is caused by particles of diameter of the order of or greater than λ (tissue cells). The intensity of scatter light is proportional to 1/λ and is predominantly forward scattering. | |
| Selectivity | Selectivity is the ability of a sensor or method to quantify accurately and specifically the analyte or analytes in the presence of other compounds. | |
| Sensitivity | Sensitivity refers to the response obtained for a given amount of analyte and is often denoted by two factors: the limit of detection and the limit of quantification. | |
| Signal-to-noise ratio | S/N | The signal to noise ratio is the ratio of the power of the signal to that of the noise. For example, in fluorimetry it would be the ratio of the square of the fluorescence intensity to the square of the intensity of the background noise. |
| Slit width | The slit width determines the amount of light entering the spectrofluorometer or spectrophotometer. A larger slit reduces the signal-to-noise ratio but reduces the wavelength resolution. | |
| Smoothing | Various methods of smoothing can be applied to improve the signal-to-noise ratio. For instance, data points recorded over time [s] or over a range of wavelengths [nm] can be smoothed by averaging n data points per interval. Then the average of the n points per smoothing interval can be taken for each successively recorded data point across the time range or range of the spectrum to give a n-point moving average smoothing. This method decreases the noise of the signal, but clearly reduces the time or wavelength resolution. More advanced methods of smoothing are applied to retain a higher time resolution or wavelength resolution. |



