|
Bioblast alert - 2021
Bioblast alert 2021(19) - Q-redox state: 2021-12-02

|
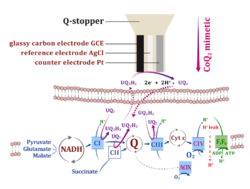
Real-time measurement of the coenzyme Q-redox state in isolated mitochondria
- Komlódi T, Cardoso LHD, Doerrier C, Moore AL, Rich PR, Gnaiger E (2021) Coupling and pathway control of coenzyme Q redox state and respiration in isolated mitochondria. Bioenerg Commun 2021.3. doi:10.26124/bec:2021-0003
- from the O2k-Network »AT Innsbruck Oroboros«
|

|
Applying Q-redox state measurements in self-assembled proteoliposome system
- Copsey AC, Barsottini MRO, May B, Xu F, Albury MS, Young L, Moore AL (2021) Kinetic characterisation and inhibitor sensitivity of Candida albicans and Candida auris recombinant AOX expressed in a self-assembled proteoliposome system. Sci Rep 11:14748. »Bioblast link«
- from the O2k-Network »UK Brighton Moore AL«
|
|
|
The central role of the Q-junction in mitochondria
The Q-junction is a point of convergence in the electron transfer system. Electrons flow from different dehydrogenases and respiratory Complexes into the Q-junction and then downstream to Complex III.
- »Q-junction«
|
|
|
Why use a short-chain coenzyme Q mimetic for measurement of the Q-redox state using the Q-Module?
The naturally occurring long-isoprenoid chain coenzyme Q (e.g. CoQ10 or CoQ9) is trapped within membrane boundaries. Therefore, a short-chain, membrane-permeable CoQ mimetic, CoQ2 is used as a probe which reacts with the mitochondrial respiratory Complexes at their quinone-binding sites and with the working electrode of the Q-sensor.
- »Coenzmye Q2« and »Q-Module«
|
Bioblast alert 2021(18) - Platelets: 2021-10-28

|
Comparison of isolation methods on mitochondrial respiration of platelets: apheresis versus density gradient centrifugation
- Vernerova A, Garcia-Souza LF, Soucek O, Kostal M, Rehacek V, Krcmova LK, Gnaiger E, Sobotka O (2021) Mitochondrial respiration of platelets: comparison of isolation methods. MitoFit Preprints 2021.6. doi:10.26124/mitofit:2021-0006
- from the O2k-Network »CZ Hradec Kralove Cervinkova Z« and »AT Innsbruck Oroboros«
|

|
Protocol for analyzing human platelet mitochondrial function in field studies
- Hoppel F, Garcia-Souza LF, Kantner-Rumplmair W, Burtscher M, Gnaiger E, Pesta D, Calabria E (2021) Human platelet mitochondrial function reflects systemic mitochondrial alterations: a protocol for application in field studies. Cells 10:2088. »Bioblast link«
- from the O2k-Network »AT Innsbruck Oroboros« »DE Duesseldorf Roden M«, »IT Verona Calabria E«
|
Bioblast alert 2021(17) - Platform comparison in fibroblast respirometry: 2021-09-29
|
|
Promoting transparency in scientific contributions
MitoFit Preprints encourages Open Access to relevant scientific contributions of acknowledged persons
»Open Access Acknowledgements«
|
Bioblast alert 2021(16) - Prostate cancer: 2021-09-16

|
A paper from the TRANSMIT project - Succinate anaplerosis enhances the malignant potential of prostate cancer cells.
- from the O2k-Network »AT Innsbruck Gnaiger E« and »FR Bordeaux Rossignol R«
- Bastos Sant'Anna Silva AC, Perez-Valencia JA, Sciacovelli M, Lalou C, Sarlak S, Tronci L, Nikitopoulou E, Meszaros AT, Frezza C, Rossignol R, Gnaiger E, Klocker H (2021) Succinate anaplerosis has an onco-driving potential in prostate cancer cells. Cancers 13:1727.»Bioblast link«
|

|
pH-regulated succinate uptake in prostate cancer
- from the O2k-Network »US PA Philadelphia Orynbayeva Z«
- Zhunussova A, Sen B, Friedman L, Tuleukhanov S, Brooks AD, Sensenig R, Orynbayeva Z (2015) Tumor microenvironment promotes dicarboxylic acid carrier-mediated transport of succinate to fuel prostate cancer mitochondria. Am J Cancer Res 5:1665-79. »Bioblast link«
|

|
Succinate: a key regulator of mitochondrial function and HIF-1α upregulation in prostate cancer
- from the O2k-Network »AT Innsbruck Oroboros«
- Weber A, Klocker H, Oberacher H, Gnaiger E, Neuwirt H, Sampson N, Eder IE (2018) Succinate accumulation is associated with a shift of mitochondrial respiratory control and HIF-1α upregulation in PTEN negative prostate cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci 19:2129. »Bioblast link«
|

|
Remodeling of OXPHOS in prostate cancer to potentially damaging mtDNA mutations and differential expression of mt-genes
- from the O2k-Network »AT Innsbruck Oroboros«
- Schöpf Bernd, Weissensteiner Hansi, Schäfer Georg, Fazzini Federica, Charoentong Pornpimol, Naschberger Andreas, Rupp Bernhard, Fendt Liane, Bukur Valesca, Giese Irina, Sorn Patrick, Sant’Anna-Silva Ana Carolina, Iglesias-Gonzalez Javier, Sahin Ugur, Kronenberg Florian, Gnaiger Erich, Klocker Helmut (2020) OXPHOS remodeling in high-grade prostate cancer involves mtDNA mutations and increased succinate oxidation. Nat Commun 11:1487. »Bioblast link«
|
Bioblast alert 2021(15) - COVID-19 & Mitochondria: 2021-09-09

|
Impaired mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle fibers of a presymptomatic COVID-19 patient
from the O2k-Network »US UT Salt Lake City Richardson R«
- Trinity JD, Craig JC, Fermoyle CC, McKenzie AI, Lewis MT, Park SH, Rondina MT, Richardson RS (2021) Impact of presymptomatic COVID-19 on vascular and skeletal muscle function: a case study. J Appl Physiol (1985) 130:1961-70. »Bioblast link«
|
|
|
Importance of mitochondrial fitness in viral infections - exercise as a protective factor for COVID-19
- from the O2k-Network »CH Lausanne Place N« and »AT Innsbruck Burtscher M«
- Burtscher J, Burtscher M, Millet GP (2021) The central role of mitochondrial fitness on antiviral defenses: An advocacy for physical activity during the COVID-19 pandemic. Redox Biol 43:1-13. »Bioblast link«
|
|
|
The mitochondria's role in the immunity of patients with SARS-CoV infections - a review from an O2k-Network lab
- from the O2k-Network »CH Lausanne Place N«
- Burtscher J, Cappellano G, Omori A, Koshiba T, Millet GP (2020) Mitochondria - in the crossfire of SARS-CoV-2 and immunity. iScience [Epub ahead of print]. »Bioblast link«
|
Bioblast alert 2021(14) - Bioenerg Commun: 2021-08-23

|
Magnesium Green™ (MgG) enables measurement of ATP production without affecting respiration
- Cardoso LHD, Doerrier C, Gnaiger E (2021) Magnesium Green for fluorometric measurement of ATP production does not interfere with mitochondrial respiration. Bioenerg Commun 2021.1. doi:10.26124/bec:2021-0001
|

|
Steps towards Open Science – from preprint to BEC manuscript with published Open Peer Reviews
BEC follows a concept of living communications with peer-reviews published non-anonymously.
- »Bioenergetics Communications«
|
Bioblast alert 2021(13) - Infectious diseases: 2021-08-13

|
Kinetic parameters of AOX proteins from Candida spp. with respect to ubiquinol-10 in a proteoliposome system – a step towards treatment development.
- from the O2k-Network »UK Brighton Moore AL«
- Copsey AC, Barsottini MRO, May B, Xu F, Albury MS, Young L, Moore AL (2021) Kinetic characterisation and inhibitor sensitivity of Candida albicans and Candida auris recombinant AOX expressed in a self-assembled proteoliposome system. Sci Rep 11:14748. »Bioblast link«
|

|
Mitochondrial function is impaired in human iPSC-derived astrocytes infected with Zika virus.
- from the O2k-Network »BR Rio de Janeiro Galina A« and »BR Rio de Janeiro Institute Biomedical Chemistry«
- Ledur PF, Karmirian K, Pedrosa CDSG, Souza LRQ, Assis-de-Lemos G, Martins TM, Ferreira JCCG, de Azevedo Reis GF, Silva ES, Silva D, Salerno JA, Ornelas IM, Devalle S, Madeiro da Costa RF, Goto-Silva L, Higa LM, Melo A, Tanuri A, Chimelli L, Murata MM, Garcez PP, Filippi-Chiela EC, Galina A, Borges HL, Rehen SK (2020) Zika virus infection leads to mitochondrial failure, oxidative stress and DNA damage in human iPSC-derived astrocytes. Sci Rep 10:1218. »Bioblast link«
|

|
Mitochondria as a treatment target for Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
- from the O2k-Network »US NC Durham Li PA«
- Lu X, Williams Z, Hards K, Tang J, Cheung CY, Aung HL, Wang B, Liu Z, Hu X, Lenaerts AJ, Woolhiser L, Hastings C, Zhang X, Wang Z, Rhee KY, Ding K, Zhang T, Cook GM (2018) A pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyridine inhibitor of the respiratory cytochrome bcc complex for the treatment of drug-resistant tuberculosis. ACS Infect Dis 5:239-49. »Bioblast link«
|
Bioblast alert 2021(12) - 4000 O2k-Publications: 2021-07-15

|
4000 O2k-Publications reached!
Well over 1000 researchers have contributed to this achievement. Send us your O2k-Publication to be added to the list.
- »O2k-Publications«
|

|
Watch the Oroboros podcast on oxygen dependence of photosynthesis and light-enhanced dark respiration
- »Podcast«
- Went N, Di Marcello M, Gnaiger E (2021) Oxygen dependence of photosynthesis and light-enhanced dark respiration studied by High-Resolution PhotoRespirometry. MitoFit Prep 2021.5. doi:10.26124/mitofit:2021-0005
|
Bioblast alert 2021(11) - Mitochondrial membrane potential: 2021-07-08
|
|
H'ow can you measure mt-membrane potential with O2k-FluoRespirometry?'
The extrinsic fluorophores safranin, TMRM or Rhodamine 123 can be used to measure mt-membrane potential in mitochondrial preparations.
- »Safranin«, »TMRM« and »Rhodamine 123«
|

|
Simultaneous measurement of O2 flux and mt-membrane potential using safranin
- from the O2k-Network »AT Innsbruck Oroboros«
- Krumschnabel G, Eigentler A, Fasching M, Gnaiger E (2014) Use of safranin for the assessment of mitochondrial membrane potential by high-resolution respirometry and fluorometry. Methods Enzymol 542:163-81.- »Bioblast link«
|
|
|
TPP+ for potentiometric detection of mt-membrane potential (mtMP) or fluorometry with safranin?
Safranin enables measurement of the relationship between fluorescence intensity and mtMP, and if linear, the absolute mtMP can be calculated. TPP+ enables calibration for measurement of mtMP.
- »TPP+ vs safranin«
|

|
Mitoquinone does not alter respiration and mt-membrane potential in obese and diabetic rats.
- from the O2k-Network »US IA Iowa City Sivitz WI«
- Fink BD, Yu L, Coppey L, Obrosov A, Shevalye H, Kerns RJ, Yorek MA, Sivitz WI (2021) Effect of mitoquinone on liver metabolism and steatosis in obese and diabetic rats. Pharmacol Res Perspect 9:e00701. »Bioblast link«
|
Bioblast alert 2021(10) - Aging: 2021-07-02

|
Downregulation of mitoNEET causes cardiac impairment in aging
- from the O2k-Network »JP Sapporo Yokota T«
- Furihata T, Takada S, Kakutani N, Maekawa S, Tsuda M, Matsumoto J, Mizushima W, Fukushima A, Yokota T, Enzan N, Matsushima S, Handa H, Fumoto Y, Nio-Kobayashi J, Iwanaga T, Tanaka S, Tsutsui H, Sabe H, Kinugawa S (2021) Cardiac-specific loss of mitoNEET expression is linked with age-related heart failure. Commun Biol 4:138. - »Bioblast link«
|

|
Potential anti-aging therapeutic target: circadian regulation of mitochondrial uncoupling
- from the O2k-Network »US FL Gainesville Hepple RT«
- Ulgherait Matt, Chen Anna, McAllister Sophie F, Kim Han X, Delventhal Rebecca, Wayne Charlotte R, Garcia Christian J, Recinos Yocelyn, Oliva Miles, Canman Julie C, Picard Martin, Owusu-Ansah Edward, Shirasu-Hiza Mimi (2020) Circadian regulation of mitochondrial uncoupling and lifespan. Nat Commun 11:1927. - »Bioblast link«
|

|
Olive polyphenols - protection against mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease and brain aging
- from the O2k-Network »DE Giessen Eckert GP«
- Grewal R, Reutzel M, Dilberger B, Hein H, Zotzel J, Marx S, Tretzel J, Sarafeddinov A, Fuchs C, Eckert GP (2020) Purified oleocanthal and ligstroside protect against mitochondrial dysfunction in models of early Alzheimer's disease and brain ageing. Exp Neurol 328:113248. - »Bioblast link«
|

|
Sugar and fat effect on initial mitochondrial aging in the brain
- from the O2k-Network »IT Naples Iossa S«
- Crescenzo R, Spagnuolo MS, Cancelliere R, Iannotta L, Mazzoli A, Gatto C, Iossa S, Cigliano L (2019) Effect of initial aging and high-fat/high-fructose diet on mitochondrial bioenergetics and oxidative status in rat brain. Mol Neurobiol 56:7651-63. - »Bioblast link«
|
Bioblast alert 2021(09) - PhotoBiology: 2021-05-19

|
Photosynthesis and respiration -
measurement of oxygen dependence of oxygen flux with high time resolution:
- Went N, Di Marcello M, Gnaiger E (2021) Oxygen dependence of photosynthesis and light-enhanced dark respiration studied by High-Resolution PhotoRespirometry. MitoFit Prep 2021.5. doi:10.26124/mitofit:2021-0005
|
|
|
How can you monitor O2 flux in response to light?
The PB-Module of the upcoming the NextGen-O2k enables experiments in PhotoBiology.
- »PB-Module« and »PhotoBiology«
|

|
7th Conference of the International Society for Applied Phycology - May 14 - August 13
May 20, 2021 at 11:00-11:30 am (GMT+2): Nora Went and Sabine Schmitt, Oroboros Instruments Q&A Session
- »ISAP 2021 Virtual«
|
Bioblast alert 2021(08) - Cell-permeable succinate: 2021-05-07

|
A cell-permeable succinate prodrug can alleviate N-methyl carbamate-induced Complex I dysfunction
- from the O2k-Network »US PA Philadelphia Kilbaugh T«, »US PA Philadelphia Jang DH« and »SE Lund Elmer E«
- Janowska JI, Piel S, Saliba N, Kim CD, Jang DH, Karlsson M, Kilbaugh TJ, Ehinger JK (2020) Mitochondrial respiratory chain Complex I dysfunction induced by N-methyl carbamate ex vivo can be alleviated with a cell-permeable succinate prodrug carbamate toxicity and treatment. Toxicol In Vitro 65:104794. - »Bioblast link«
|

|
Cell-permeable succinate can restore statin-inhibited mitochondrial respiration
- from the O2k-Network »RO Timisoara Muntean DM« and »SE Lund Elmer E«
- Avram VF, Chamkha I, Åsander-Frostner E, Ehinger JK, Timar RZ, Hansson MJ, Muntean DM, Elmér E (2021) Cell-permeable succinate rescues mitochondrial respiration in cellular models of statin toxicity. Int J Mol Sci 22:424. - »Bioblast link«
|
Bioblast alert 2021(07) - Diabetes: 2021-04-15

|
Diabetes, infarct size, mitochondrial respiration and succinate dehydrogenase inhibition - how do they relate?
- from the O2k-Network »DK Aarhus Boetker HE«
- Tonnesen PT, Hjortbak MV, Lassen TR, Seefeldt JM, Bøtker HE, Jespersen NR (2021) Myocardial salvage by succinate dehydrogenase inhibition in ischemia-reperfusion injury depends on diabetes stage in rats. Mol Cell Biochem [Epub ahead of print]. - »Bioblast link«
|

|
Gastric bypass surgery improves diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetic rats
- from the O2k-Network »CN Chongqing Zhu Z«
- Wei X, Lu Z, Li L, Zhang H, Sun F, Ma H, Wang L, Hu Y, Yan Z, Zheng H, Yang G, Liu D, Tepel M, Gao P, Zhu Z (2020) Reducing NADPH synthesis counteracts diabetic nephropathy through restoration of AMPK activity in type 1 diabetic rats. Cell Rep 32:108207. - »Bioblast link«
|

|
Skeletal muscle mitochondrial bioenergetics in men and women with type 1 diabetes
- from the O2k-Network »CA Toronto Perry CG«
- Monaco CMF, Bellissimo CA, Hughes MC, Ramos SV, Laham R, Perry CGR, Hawke TJ (2020) Sexual dimorphism in human skeletal muscle mitochondrial bioenergetics in response to type 1 diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 318:E44-E51. - »Bioblast link«
|
Bioblast alert 2021(06) - Fatty acid oxidation (FAO): 2021-03-19

|
Approved FAO inhibitor Trimetazidine restricts tumor growth in oxidative lung carcinomas
- from the O2k-Network »FR Bordeaux Rossignol R«
- Amoedo ND, Sarlak S, Obre E, Esteves P, Bégueret H, Kieffer Y, Rousseau B, Dupis A, Izotte J, Bellance N, Dard L, Redonnet-Vernhet I, Punzi G, Rodrigues MF, Dumon E, Mafhouf W, Guyonnet-Dupérat V, Gales L, Palama T, Bellvert F, Dugot-Senan N, Claverol S, Baste JM, Lacombe D, Rezvani HR, Pierri CL, Mechta-Grigoriou F, Thumerel M, Rossignol R (2021) Targeting the mitochondrial trifunctional protein restrains tumor growth in oxidative lung carcinomas. J Clin Invest 131:e133081. - »Bioblast link«
|

|
Quantifying FAO capacity (F-pathway) - avoid overestimation
Malate anaplerotic pathways are active in various tissues and cultured cells, which can lead to an overestimation of the F-pathway capacity. .
- Evaluate the malate anaplerotic pathway: »SUIT-027«
- Analyze F-pathway avoiding overestimation: »SUIT-002« and »SUIT-025«
|
Bioblast alert 2021(05) - Bioenerg Commun & MitoFit Preprints: 2021-03-04

|
Mitochondrial physiology in Parkinson’s disease (PD)
A COST Action MitoEAGLE contribution:
- Krako Jakovljevic N, Ebanks B, Chakrabarti L, Markovic I, Moisoi N (2021) Mitochondrial homeostasis in cellular models of Parkinson’s Disease. MitoFit Preprints 2021.4 doi:10.26124/mitofit:2021-0004
|

|
Internal normalization of rate – what is the difference between flux control ratio and flux control efficiency?
A flux control ratio is the ratio of oxygen flux in a specific respiratory control state, normalized for maximum flux in a common reference state. Flux control efficiency expresses the control of respiration as a fractional change of oxygen flux or flow between protocol steps. Both values vary between theoretical lower and upper limits of 0 and 1.
- »Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways - Chapter 3«
|

|
Submit manuscripts simultaneously to MitoFit Preprints and Bioenergetics Communications via the BEC website
A seamless process for taking MitoFit preprints to living BEC communications with open and published peer review.
- »Bioenergetics Communications«
|
Bioblast alert 2021(04) - MitoFit Preprints: 2021-02-19

|
Exploring the Q-junction in real-time
Simultaneous measurement of coenzyme Q redox state and respiration in isolated mitochondria:
- Komlodi T, Cardoso LHD, Doerrier C, Gnaiger E (2021) Coupling and pathway control of coenzyme Q redox state and respiration in isolated mitochondria. MitoFit Preprints 2021.2. doi:10.26124/mitofit:2021-0002
|

|
Diagnosis of mitochondrial disease in frozen samples
Measurement of respiratory function in cryopreserved muscle biopsies:
- Zuccolotto-dos-Reis FH, Andriao-Escarso SH, Araujo JS, Espreafico EM, Alberici LC, Sobreira CFR (2021) Acetyl CoA driven respiration in frozen muscle contributes to the diagnosis of mitochondrial disease. MitoFit Preprints 2021.3. doi:10.26124/mitofit:2021-0003
|
Bioblast alert 2021(03) - ATP production P»: 2021-01-29

|
SUIT protocols with Magnesium Green™ (MgG) can be used to study respiration and ATP production P»
MgG dye does not affect respiration of cardiac isolated mitochondria.
- Cardoso LHD, Doerrier C, Gnaiger E (2021) Magnesium Green for fluorometric measurement of ATP production does not interfere with mitochondrial respiration. MitoFit Preprints 2021.1. doi:10.26124/mitofit:2021-0001
|

|
Measuring ATP-ADP exchange using the fluorophore Magnesium Green
- from the O2k-Network »HU Budapest Chinopoulos C«
- Chinopoulos C, Kiss G, Kawamata H, Starkov AA (2014) Measurement of ADP-ATP exchange in relation to mitochondrial transmembrane potential and oxygen consumption. Methods Enzymol 542:333-48. »Bioblast link«
|
|
|
Magnesium Green and P» – which sample preparations work?
Magnesium Green (MgG) can be used with mitochondrial preparations: isolated mitochondria, tissue homogenates, and permeabilized cells and tissues.
- »MgG« and »Publications MgG«
|
Bioblast alert 2021(02) - Permeabilized fibers: 2021-01-21

|
A quote from MitoPathways Chapter 3. Normalization:
Respiratory OXPHOS capacity P in human skeletal muscle ranges from 60 to 160 pmol∙s-1∙mg-1 based on wet muscle mass of permeabilized fibers. By comparison, mass-specific electron transfer capacity E is approximately 25 pmol∙s-1∙mg-1 in platelets and senescent fibroblasts and 40 to 80 pmol∙s-1∙mg-1 in PBMC, HEK, CEM, HUVEC, and young fibroblasts. ― Are these values comparable? - »Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways«.
|

|
Statistical evaluation on replica in high-resolution respirometry with permeabilized skeletal muscle fibers
- from the O2k-Network »AU Melbourne Bishop DJ«
- Jacques M, Kuang J, Bishop DJ, Yan X, Alvarez-Romero J, Munson F, Garnham A, Papadimitriou I, Voisin S, Eynon N (2019) Mitochondrial respiration variability and simulations in human skeletal muscle: The Gene SMART study. FASEB J 34:2978-86. - »Bioblast link«
|

|
Effect of temperature on mitochondrial respiratory capacity of cardiac permeabilized fibers
- from the O2k-Network »AT Innsbruck Gnaiger E« , »CA Rimouski Blier PU« and »CA Edmonton Lemieux H«
- Lemieux H, Blier PU, Gnaiger E (2017) Remodeling pathway control of mitochondrial respiratory capacity by temperature in mouse heart: electron flow through the Q-junction in permeabilized fibers. Sci Rep 7:2840. »Bioblast link«
|
|
|
What is the optimal ADP concentration to evaluate OXPHOS capacity in permeabilized muscle fibers (pfi)?
For the evaluation of OXPHOS capacity, the limitation of respiratory fluxes must be avoided by using a kinetically-saturating ADP concentration. In permeabilized muscle fibers, an ADP concentration of 5 mM or higher is needed to reach kinetically-saturating levels.
- »Optimum ADP concentration in pfi«
|
Bioblast alert 2021(01) - MitoPathways: the new BEC edition of the Blue Book: 2021-01-05

|
The 5th edition of MitoPathways features new chapters on additivity of mitochondrial pathway capacities and protonmotive pressure – one step beyond ∆Ψ and the protonmotive force.
|
|
|
Summary
Bioblast alert - previous issues
Stay alert
|