Semantic search
| Term | Abbreviation | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Microsyringe\500 mm3\TIP2k | Microsyringe\500 mm3\TIP2k: Microinjection syringe for Titration-Injection microPump, 500 mm3 (µl), fixed injection needle with rounded tip, with spacers. | |
| Microxia | microx | Microxia (deep hypoxia) is obtained when trace amounts of O2 exert a stimulatory effect on respiration above the level where metabolism is switched to a purely anaerobic mode. |
| MitObesity drugs | Bioactive mitObesity compounds are drugs and nutraceuticals with more or less reproducible beneficial effects in the treatment of diverse preventable degenerative diseases implicated in comorbidities linked to obesity, characterized by common mechanisms of action targeting mitochondria. | |
| MitoAction | MitoAction |  The mission of MitoAction is to improve quality of life for all who are affected by mitochondrial disorders through support, education and advocacy initiatives. The mission of MitoAction is to improve quality of life for all who are affected by mitochondrial disorders through support, education and advocacy initiatives. |
| MitoCanada Foundation | mitoCanada | The MitoCanada Foundation. The MitoCanada Foundation is Canada’s only not-for-profit organization focused on mitochondrial disease. Since its founding in 2010, MitoCanada has dedicated over $1 million to fund the work of leading Canadian scientists and to support national awareness and support programs. The MitoCanada Foundation is committed to ensuring that those who live with mitochondrial disease are able to enjoy the best possible quality of life until there is a cure. |
| MitoFit DOI Data Center | MitoFit DOI DC | The MitoFit DOI Data Center is responsible for the provision of digital identifiers, for the storage and ensuring the persistence of the scientific objects, the provision of access, review process and maintenance of the Metadata, and quality control. |
| MitoFit Preprints | MitoFit Prep | MitoFit Preprints is an Open Access preprint server for mitochondrial physiology and bioenergetics. |
| MitoFit protocols | MitoFit protocols are moderated by the MitoFit moderators (MitoFit team), either as protocols with direct reference to publications available to the scientific communicty, or protocols additionally described and made available in Bioblast with full information on authors (including contact details), author contributions, and editor (moderator) in charge. This aims at a comprehensive MitoFit data repository, which will require global input and cooperation. | |
| MitoFit registered project | MitoFit-RP | MitoFit registered projects are announced with reference to MitoFit protocols as publicly deposited protocols. Project registration is a two-phase process. Guidelines will be defined. (1) Pre-registration of a project requires submission to a MitoFit moderator (editor), including protocol details with reference to MitoPedia protocols, or with submission of protocols for publication (Open Access) in MitoPedia. The MitoFit (Bioblast) editors will edit the submitted protocols (layout) and insert into Bioblast submitted pre-registrations and protocols. (2) MitoFit moderators (editors) will set up a MitoFit accreditation panel, in which the registrant will be included (perhaps not in the long run, to avoid conflict of interests) and/or for which the registrant can suggest delegates (compare peer review). Accredited MitoFit protocols are labelled as MitoFit accredited, and the pre-registered MitoFit project becomes labelled and listed as MitoFit registered project (MitoFit accredited). This is possible before (advance registration), during progress, and after completion of a study (post-registration). A MitoFit registered project receives a code for feeding data into the MitoFit data repository. |
| MitoGlobalPlayer invitation | ||
| MitoKit-CII | Cell permeable prodrugs, composed of MitoKit-CII/Succinate-nv and MitoKit-CII/Malonate-nv, stimulates (Snv) or inhibits (Mnanv) mitochondrial respiration in CI-deficient human blood cells, fibroblasts and heart fibres, acting on Complex II of the electron transfer system. | |
| MitoKit-CII/Malonate-nv | Mnanv | MitoKit-CII/Malonate-nv (diacetoxymethyl malonate) is a plasma membrane-permeable prodrug (permeable malonate; Mnanv) that diffuses across the plasma membrane. Cleavage of diacetoxymethyl groups is mediated by intracellular esterases, thus releasing malonate in the intracellular space. Abliva #: 01-161-s2 |
| MitoKit-CII/Succinate-nv | Snv | MitoKit-CII/Succinate-nv (diacetoxymethyl succinate) is a plasma membrane-permeable prodrug (permeable succinate; Snv) that diffuses across the plasma membrane. Cleavage of diacetoxymethyl groups is mediated by intracellular esterases, thus releasing succinate in the intracellular space. Abliva #: 01-118-s4 |
| MitoOx1 | MitoOx1 | Mitochondrial respiration medium, MitoOx1, used by the Budapest groups for respirometry und Amplex Red trials. |
| MitoOx2 | MitoOx2 | Mitochondrial respiration medium, MitoOx2, developed for oxygraph incubations of mitochondrial preparations to measure the H2O2 production. MitoOx2 yields a higher optical sensitivity and lower "drift" (oxidation of the fluorophore precurcor without H2O2 present) for Amplex UltraRed(R) than e.g. MiR05. |
| MitoPedia | ||
| MitoPedia | ||
| MitoPedia: Concepts and methods | ||
| MitoPedia: Enzymes | ||
| MitoPedia: Ergodynamics | ||
| MitoPedia: Fluorometry | ||
| MitoPedia: Gentle Science | ||
| MitoPedia: Inhibitors | ||
| MitoPedia: Media for respirometry | ||
| MitoPedia: MiP and biochemistry | ||
| MitoPedia: MiP concepts | ||
| MitoPedia: O2k hardware | ||
| MitoPedia: Oroboros QM | ||
| MitoPedia: Permeabilization agents | ||
| MitoPedia: Preprints and history | ||
| MitoPedia: Respiratory control ratios | ||
| MitoPedia: Respiratory states | ||
| MitoPedia: Respirometry | ||
| MitoPedia: SUIT A | ||
| MitoPedia: SUIT B | ||
| MitoPedia: SUIT C | ||
| MitoPedia: Sample preparations | ||
| MitoPedia: Spectrophotometry | ||
| MitoPedia: Substrates and metabolites | ||
| MitoPedia: Uncouplers | ||
| MitoSOX | MitoSOXTM is the version of the hydroetidine designed to target mitochondria in live cells for the detection of superoxide (O2•-). The oxidation of the compound by O2•- is easily detected in the red spectrum. One of the advantages of MitoSOXTM is its selectivity for O2•- but not for other reactive oxygen species or reactive nitrogen species.
| |
| Mitochondria | mt | Mitochondria (Greek mitos: thread; chondros: granule) are small structures within cells, which function in cell respiration as powerhouses or batteries. Mitochondria belong to the bioblasts of Richard Altmann. Abbreviation: mt, as generally used in mtDNA. Singular: mitochondrion (bioblast); plural: mitochondria (bioblasts). |
| Mitochondria Interest Group | MIG |
The Mitochondria Interest Group (MIG) is an Inter-Institute Interest Group at the National Institutes of Health (NIH), with members worldwide! MIG is concerned with all aspects of the mitochondrion and diseases in which the mitochondrion is involved. We hold monthly meetings, usually on the second Monday of the month (except when it is a Federal holiday or other special exceptions). MITOCHONDRIA-L@LIST.NIH.GOV is an Email list moderated by Ph.D. Steven Zullo as an interactive information platform, with free subscritpion to this mitochondrial network. List members are reminded of their responsibility to critically evaluate the content of the postings. The information, opinions, data, and statements contained herein are not necessarily those of the U. S. Government, the National Institutes of Health (NIH), or MIG and should not be interpreted, acted on or represented as such. |
| Mitochondria Research Society | MRS |
The Mitochondria Research Society (MRS) is a nonprofit international organization of scientists and physicians. The purpose of MRS is to find a cure for mitochondrial diseases by promoting research on basic science of mitochondria, mitochondrial pathogenesis, prevention, diagnosis and treatment through out the world. |
| Mitochondria-Targeted Drug Development | hansonwade |
The Mitochondria-Targeted Drug Development Summit was first established in 2021, as an online conference. Due to its success and unmatched focus, the 2nd edition returns to Boston this March 2022. This is the only industry-led meeting that unites key stakeholders under a mutual and ambitious objective of accelerating the discovery and development of novel drugs that target mitochondrial functions for chronic, primary mitochondrial diseases, muscular dystrophy, metabolic disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases. Join our speakers from GenSight Biologics, Abliva, Reneo Pharma, Mito BioPharma, Mitokinin and more with exciting networking opportunities, panel discussions and dedicated roundtables. |
| Mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K+ channel | mtKATP | The mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K+ channel (mtKATP or mitoKATP). |
| Mitochondrial European Education Training | MEET | The Mitochondrial European Education Training (MEET) MEET is a project started on January 2013. MEET network is composed by a multi-partner project that intends to mobilize the critical mass of expertise, by linking partners from 8 different countries, among which 8 world-leading basic science and clinical centers of excellence, an 1 SME with direct interest in mitochondrial medicine and 3 associated partners that provide for all trainees no-scientific training. MEET is training 11 ESRs and 3 ERs coming from all over the world supervised in their research by 15 mentors and by their collaborators. MEET combine the efforts of leading clinicians with those of more basic oriented groups and will have important implications for the comprehension and treatment of mitochondria-related pathologies. |
| Mitochondrial Medicine Society | MMS |
The Mitochondrial Medicine Society (MMS) was founded in 2000 and represents an international group of physicians, researchers and clinicians working towards the better diagnosis, management, and treatment of mitochondrial diseases. |
| Mitochondrial Physiology Network | Mitochondr physiol network, MiPNet | The Mitochondrial Physiology Network is the on-line Oroboros journal. |
| Mitochondrial Research Guild |
The Mitochondrial Research Guild is a special interest guild of Seattle Children's Hospital. The guild was founded by a group of families in the Seattle area that are working together to raise awareness, promote research, and improve the quality of medical care that is available to children that are dealing with the devastating and potentially life threatening effects of mitochondrial disease. | |
| Mitochondrial competence | mt-competence; MitoCom | Mitochondrial metabolic competence is the organelle's capacity to provide adequate amounts of ATP in due time, by adjusting the mt-membrane potential, mt-redox states and the ATP/ADP ratio according to the metabolic requirements of the cell. The term mitochondrial competence is also known in a genetic context: Mammalian mitochondria possess a natural competence for DNA import. MitoCom_O2k-Fluorometer is a Mitochondrial Competence network, the nucleus of which is formed by the K-Regio project MitoCom Tyrol. |
| Mitochondrial concentration | CmtE | Mitochondrial concentration is CmtE = mtE·V-1 [mtEU·m-3]. mt-Concentration is an experimental variable, dependent on sample concentration. |
| Mitochondrial content | mtENX | Mitochondrial content per object X is mtENX = mtE·NX-1 [mtEU·x-1]. |
| Mitochondrial density | DmtE | Specific mitochondrial density is DmtE = mtE·mX-1 [mtEU·kg-1]. If the amount of mitochondria, mtE, is expressed as mitochondrial mass, then DmtE is the mass fraction of mitochondria in the sample. If mtE is expressed as mitochondrial volume, Vmt, and the mass of sample, mX, is replaced by volume of sample, VX, then DmtE is the volume fraction of mitochondria in the sample. |
| Mitochondrial free radical theory of aging | MFRTA | The mitochondrial free radical theory of aging goes back to Harman (1956) and ranks among the most popular theories of aging. It is based on postulates which are not unequivocally supported by observation (Bratic, Larsson 2013): (i) Mitochondrial ROS production increases with age caused by progressive mitochondrial dysfunction; (ii) antioxidat capacity declines with age; (iii) mutations of somatic mtDNA accumulate during aging; (iv) a vicious cycle occurs of increased ROS production caused by mtDNA mutations and degenerated mt-function, and due to ROS-induced ROS production. |
| Mitochondrial inner membrane | mtIM | The mitochondrial inner membrane mtIM is the structure harboring the membrane-bound electron transfer system ETS including the respiratory complexes working as hydrogen ion pumps, the mt-phosphorylation system including the hydrogen ion pump ATP synthase, several substrate transporters involved in the electron transfer pathway, and a variety of other ion pumps that carry proton charge (Ca2+, Mg2+). The protonmotive force is the electrochemical potential difference across the mtIM generated by the hydrogen ion pumps of the . |
| Mitochondrial marker | mt-marker | Mitochondrial markers are structural or functional properties that are specific for mitochondria. A structural mt-marker is the area of the inner mt-membrane or mt-volume determined stereologically, which has its limitations due to different states of swelling. If mt-area is determined by electron microscopy, the statistical challenge has to be met to convert area into a volume. When fluorescent dyes are used as mt-marker, distinction is necessary between mt-membrane potential dependent and independent dyes. mtDNA or cardiolipin content may be considered as a mt-marker. Mitochondrial marker enzymes may be determined as molecular (amount of protein) or functional properties (enzyme activities). Respiratory capacity in a defined respiratory state of a mt-preparation can be considered as a functional mt-marker, in which case respiration in other respiratory states is expressed as flux control ratios. » MiPNet article |
| Mitochondrial marker enzymes | Mitochondrial marker enzymes are enzymes that are specifically present in mitochondria, in the mt-matrix, the inner mt-membrane, the inter-membrane space, or the outer mt-membrane. | |
| Mitochondrial matrix | mt-matrix | The mitochondrial matrix (mt-matrix) is enclosed by the mt-inner membrane mtIM. The terms mitochondrial matrix space or mitochondrial lumen are used synonymously. The mt-matrix contains the enzymes of the tricarboxylic acid cycle, fatty acid oxidation and a variety of enzymes that have cytosolic counterparts (e.g. glutamate dehydrogenase, malic enzyme). Metabolite concentrations, such as the concentrations of fuel substrates, adenylates (ATP, ADP, AMP) and redox systems (NADH), can be very different in the mt-matrix, the mt-intermembrane space, and the cytosol. The finestructure of the gel-like mt-matrix is subject of current research. |
| Mitochondrial membrane potential | mtMP, ΔΨp+, ΔelFep+ [V] | The mitochondrial membrane potential difference, mtMP or ΔΨp+ = ΔelFep+, is the electric part of the protonmotive force, Δp = ΔmFeH+.
ΔΨp+ is the potential difference across the mitochondrial inner membrane (mtIM), expressed in the electric unit of volt [V]. Electric force of the mitochondrial membrane potential is the electric energy change per ‘motive’ charge or per charge moved across the transmembrane potential difference, with the number of ‘motive’ charges expressed in the unit coulomb [C]. |
| Mitochondrial outer membrane | mtOM | The mitochondrial outer membrane is the incapsulating membrane which is osmotically not active and contains the cytochrome b5 enzyme similar to that found in the endoplasmatic reticulum, the translocases of the outer membrane, monoaminooxidase, the palmitoyl-CoA synthetase and carnytil-CoA transferase 1. |
| Mitochondrial preparations | mtprep | Mitochondrial preparations (mtprep) are isolated mitochondria (imt), tissue homogenate (thom), mechanically or chemically permeabilized tissue (permeabilized fibers, pfi) or permeabilized cells (pce). In mtprep the plasma membranes are either removed (imt) or mechanically (thom) and chemically permeabilized (pfi), while mitochondrial functional integrity and to a large extent mt-structure are maintained in incubation media optimized to support mitochondrial physiological performance. According to this definition, submitochondrial particles (smtp) are not a mtprep, since mitochondrial structure is altered although specific mitochondrial functions are preserved. |
| Mitochondrial respiration | Integrative measure of the dynamics of complex coupled metabolic pathways, including metabolite transport across the mt-membranes, TCA cycle function with electron transfer through dehydrogenases in the mt-matrix, membrane-bound electron transfer mET-pathway, the transmembrane proton circuit, and the phosphorylation system. | |
| Mitochondrial respiration media: comparison | MiR | Mitochondrial respiratory capacity and control are compared in different mitochondrial respiration media, MiRs, to evaluate the quality of MiRs in preserving mitochondrial function and to harmonize results obtained in various studies using different MiRs. In some cases alterations of the formulation are incorporated to optimize conditions for the simultaneous measurement of multiple parameters, e.g. respiration and ROS production. |
| Mitochondrial states and rates - terminology beyond MitoEAGLE 2020 | States and rates | 666 coauthors of the 'MitoEAGLE white paper' [1] collaborated to reach a consensus on terminology related to mitochondrial respiratory states and rates. This page is intended to prepare a questionnaire and follow-up publication. |
| Mitochondrial transcription factor A | TFAM | The transcription factor A is a gene that encodes a mitochondrial transcription factor that is a key activator of mitochondrial transcription as well as a participant in mitochondrial genome replication. TFAM is downstream of PGC-1alpha. |
| Mitophagy | Autophagy (self-eating) in general is viewed as a degradation process which removes non-essential or damaged cellular constituents. » MiPNet article | |
| Model | A model regarding databases is the representation of a real world object in a computer understandable language. A model can be defined by the structure of its dataset and the relations to other models. | |
| Molar mass | M [kg·mol-1]; [g·mol-1] | Molar mass M is the mass of a chemical compound divided by its amount-of-substance measured in moles. It is defined as MB = m/nB, where m is the total mass of a sample of pure substance and nB is the amount of substance B given in moles. The definition applies to pure substance. The molar mass allows for converting between the mass of a substance and its amount for bulk quantities. It is calculated as the sum of standard atomic weights of all atoms that form one entity of the substance. The appropriate SI base units is kg·mol-1. However, for historical as well as usability reasons, g·mol-1 is almost always used instead. |
| Mole | mol | The mole [mol] is the SI base unit for the amount of substance of a system that contains 6.02214076·1023 specified elementary entities (see Avogadro constant). The elementary entities must be specified and may be atoms, molecules, ions, electrons, other particles, or specified groups of such particles. |
| Monoamine oxidase | MAO | Monoamine oxidases are enzymes bound to the outer membrane of mitochondria and they catalyze the oxidative deamination of monoamines. Oxygen is used to remove an amine group from a molecule, resulting in the corresponding aldehyde and ammonia. Monoamine oxidases contain the covalently bound cofactor FAD and are, thus, classified as flavoproteins. |
| Motic Microscope | Motic Microscope SMZ-171 TLED: for preparation of permeabilized fibres; compact and light stereo microscope, Greenough optical system, switching power supply for use worldwide (100-240V); including auxiliary ESD objective 2.0X(38.6mm). | |
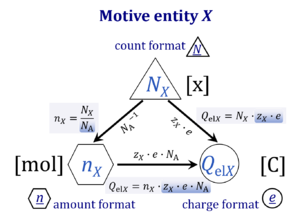
| Motive entity | Xtr [MU] | . A motive entity Xtr is an entity involved in a transformation including spacial transfer. Motive entities (transformants) are expressed in different motive units [MU] depending on the energy transformation under study and the chosen format. Flows are defined as advancement in terms of stoichiometric motive entities per time. Isomorphic forces are partial derivatives of Gibbs energy per advancement. Ions carrying a positive charge (cations) or negative charge (anions) may be considered as a paradigm of motive entities, since Faraday did not coin but introduced the term 'ion', which is old Greek for 'going' — advancing to the cathode or anode and thus generating an electric current. |
| Motive unit | MU | The motive unit [MU] is the variable SI unit in which the motive entity (transformant) of a transformation is expressed, which depends on the energy transformation under study and on the chosen format. Fundamental MU for electrochemical transformations are:
For the protonmotive force the motive entity is the proton with charge number z=1. The protonmotive force is expressed in the electrical or molar format with MU J/C=V or J/mol=Jol, respectively. The conjugated flows, I, are expressed in corresponding electrical or molar formats, C/s = A or mol/s, respectively. The charge number, z, has to be considered in the conversion of motive units (compare Table below), if a change not only of units but a transition between the entity elementary charge and an entity with charge number different from unity is involved (e.g., O2 with z=4 in a redox reaction). The ratio of elementary charges per reacting O2 molecule (zO2=4) is multiplied by the elementary charge (e, coulombs per proton), which yields coulombs per O2 [C∙x-1]. This in turn is multiplied with the Avogadro constant, NA (O2 molecules per mole O2 [x∙mol-1]), thus obtaining for zeNA the ratio of elementary charges [C] per amount of O2 [mol-1]. The conversion factor for O2 is 385.94132 C∙mmol-1. |
| Mouse control: Mark | Ctrl+M | The mark mode is active by default, can be selected in the menu or by [Ctrl+M]. If Mouse control: Mark is enabled, specific sections of the experiment can be marked in each plot. Usually, marks are set on the plot for oxygen concentration for calibration, whereas marks on the plot for oxygen flux are set for exporting the median or average of flux to a table. »More details: Marks - DatLab. |
| Mouse control: Zoom | Ctrl+Z | Select Mouse Control: Zoom in the Graph-menu or press [Ctrl+Z]. |
| MtOM | mtOM | The mitochondrial outer membrane |
| MultiSensor-Connector |
MultiSensor-Connector: for separate reference electrode and ISE; only for O2k-Series B and Series C with MultiSensor electronic upgrading before 2011. | |
| MultiSensor-Preamplifier 1/100 |
MultiSensor-Preamplifier 1/100: Required only for O2k-Series A-C, for application of NO (or other amperometric) sensors (single chamber mode of application). | |
| Multicomponent analysis | Similarly to the least squares method, multicomponent analysis makes use of all of the data points of the spectrum in order to analyse the concentration of the component parts of a measured spectrum. To do this, two or more reference spectra are combined using iterative statistical techniques in order to achieve the best fit with the measured spectrum. | |
| Myxothiazol | Myx | Myxothiazol Myx is an inhibitor of Complex III (CIII). CIII also inhibits CI. Myxothiazol binds to the Qo site of CIII (close to cytochrome bL) and inhibits the transfer of electrons from reduced QH2 to the Rieske iron sulfur protein. |
| N-ethylmaleimide | Nem | N-ethylmaleimide is an organic compound that is derived from maleic acid and blocks endogenous Pi transport. |
| N-junction |
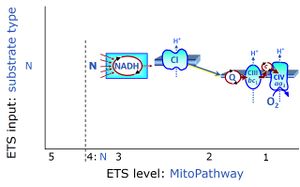
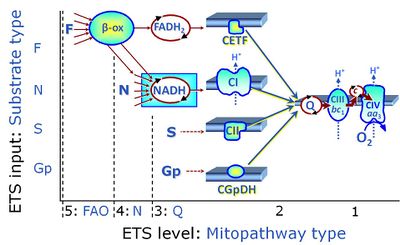
The N-junction is a junction for convergent electron flow in the electron transfer pathway (ET-pathway) from type N substrates (further details »N-pathway control state) through the mt-NADH pool to Complex I (CI), and further transfer through the Q-junction to Complex III (CIII). Representative type N substrates are pyruvate (P), glutamate (G) and malate (M). The corresponding dehydrogenases (PDH, GDH, MDH) and some additional TCA cycle dehydrogenases (isocitrate dehydrogenase, oxoglutarate dehydrogenase generate NADH, the substrate of Complex I (CI). The concept of the N-junction and F-junction provides a basis for defining categories of SUIT protocols based on Electron-transfer-pathway states. | |
| N/NS pathway control ratio | N/NS | The N/NS pathway control ratio is obtained when succinate is added to N-linked respiration in a defined coupling state. N and NS are abbreviations for respiration in the N-pathway control state (with pyruvate, glutamate, malate, or other ETS competent N-linked substrate combinations) and the NS-pathway control state (N in combination with succinate). NS indicates respiration with a cocktail of substrates supporting the N- and S-pathways. |
| N/S pathway control ratio | N/S | The N/S pathway control ratio is obtained from SUIT protocols when the N-pathway flux and S-pathway flux are measured in the same coupling control state. The N/S pathway control ratio may be larger or smaller than 1.0, depending on the mitochondrial source and various mitochondrial injuries. The S-pathway control state may be selected preferentially as reference state, if mitochondria are studied with respect to N-pathway injuries. |
| NADH | NADH | NAD+ and NADH: see Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. |
| NADH calibration - DatLab | NADH calibration | |
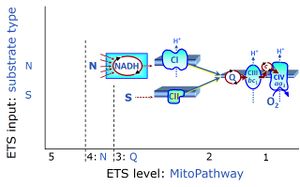
| NADH electron transfer-pathway state | N |
The NADH electron transfer-pathway state (N) is obtained by addition of NADH-linked substrates (CI-linked), feeding electrons into the N-junction catalyzed by various mt-dehydrogenases. N-supported flux is induced in mt-preparations by the addition of NADH-generating substrate combinations of pyruvate (P), glutamate (G), malate (M), oxaloacetate (Oa), oxoglutarate (Og), citrate, hydroxybutyrate. These N-junction substrates are (indirectly) linked to Complex I by the corresponding dehydrogenase-catalyzed reactions reducing NAD+ to NADH+H+ + H+. The most commonly applied N-junction substrate combinations are: PM, GM, PGM. The malate-anaplerotic pathway control state (M alone) is a special case related to malic enzyme (mtME). The glutamate-anaplerotic pathway control state (G alone) supports respiration through glutamate dehydrogenase (mtGDH). Oxidation of tetrahydrofolate is a NAD(P)H linked pathway with formation of formate. In mt-preparations, succinate dehydrogenase (SDH; CII) is largely substrate-limited in N-linked respiration, due to metabolite depletion into the incubation medium. The residual involvement of S-linked respiration in the N-pathway control state can be further suppressed by the CII-inhibitor malonic acid). In the N-pathway control state ET pathway level 4 is active. |
| NADH fluorescence | Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) is amongst the intrinsic fluorophores and can be used as an intracellular indicator of hypoxia. The excitation wavelength is 340 nm and emission is at 460 nm. | |
| NADH-Module | The NADH-Module, is a component of the NextGen-O2k for simultaneous measurement of oxygen consumption and NAD(P)H autofluorescence. NAD(P)H autofluorescence is used to evaluate the redox state of the NAD(P)H-pool. The NADH-Module incorporates an UV light and NADH-Sensors which include a photodiode and specific filters. | |
| NADH-Sensor | The NADH-Sensor has been developed as a part of the NADH-Module for simultaneous monitoring of oxygen consumption and NADH redox state. The NADH-Sensor is composed of a photodiode and equipped with three supergel R370 Italian blue filters (Rosco, US). | |
| NCD-RisC 2017 Lancet | ||
| NS e-input | NS, CI&II | NS e-input or the NS-pathway control state is electron input from a combination of substrates for the N-pathway control state and S-pathway control state through Complexes CI and CII simultaneously into the Q-junction. NS e-input corresponds to TCA cycle function in vivo, with convergent electron flow through the Electron transfer pathway. In mt-preparations, NS e-input requires addition not only of NADH- (N-) linked substrates (pyruvate&malate or glutamate&malate), but of succinate (S) simultaneously, since metabolite depletion in the absence of succinate prevents a significant stimulation of S-linked respiration. For more details, see: Additive effect of convergent electron flow. |
| NS-N pathway control efficiency | jNS-N; jCI&II-CI | The NS-N pathway control efficiency, jNS-N = 1-N/NS, expresses the fractional change of flux when succinate is added to the N-pathway control state in a defined coupling-control state. |
| NS-S pathway control efficiency | jNS-S | The NS-S pathway control efficiency expresses the relative stimulation of succinate supported respiration (S) by NADH-linked substrates (N), with the S-pathway control state as the background state and the NS-pathway control state as the reference state. In typical SUIT protocols with type N and S substrates, flux in the NS-pathway control state NS is inhibited by rotenone to measure flux in the S-pathway control state, S(Rot) or S. Then the NS-S pathway control efficiency in the ET-coupling state is j(NS-S)E = (NSE-SE)/NSE The NS-S pathway control efficiency expresses the fractional change of flux in a defined coupling-control state when inhibition by rotenone is removed from flux under S-pathway control in the presence of a type N substrate combination. Experimentally rotenone Rot is added to the NS-state. The reversed protocol, adding N-substrates to a S-pathway control background does not provide a valid estimation of S-respiration with succinate in the absence of Rot, since oxaloacetate accumulates as a potent inhibitor of succinate dehydrogenase CII. |
| NS-pathway control state | NS, CI&II |
NS-pathway control is exerted in the NS-linked substrate state (flux in the NS-linked substrate state, NS; or Complex I&II, CI&II-linked substrate state). NS-OXPHOS capacity provides an estimate of physiologically relevant maximum mitochondrial respiratory capacity. NS is induced in mt-preparations by addition of NADH-generating substrates (N-pathway control state in combination with succinate (Succinate pathway; S). Whereas NS expresses substrate control in terms of substrate types (N and S), CI&II defines the same concept in terms of convergent electron transfer to the Q-junction (pathway control). NS is the abbreviation for the combination of NADH-linked substrates (N) and succinate (S). This physiological substrate combination is required for partial reconstitution of TCA cycle function and convergent electron-input into the Q-junction, to compensate for metabolite depletion into the incubation medium. NS in combination exerts an additive effect of convergent electron flow in most types of mitochondria. |
| NSGp | NSGp |
MitoPathway control state: NSGp
SUIT protocol: SUIT-038 This substrate combination supports convergent electron flow to the Q-junction. |
| Nagarse | Nagarse is a broad specifity protease from bacteria used to promote breakdown of the cellular structure of "hard" tissues such as skeletal muscle or heart mucsle that cannot be homogenized easily without treatment with a protease. Nagarse is frequently used in protocols for isolating mitochondria from muscle tissue. | |
| National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine 2023 BMI and beyond | ||
| National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine 2024 Body composition and obesity |